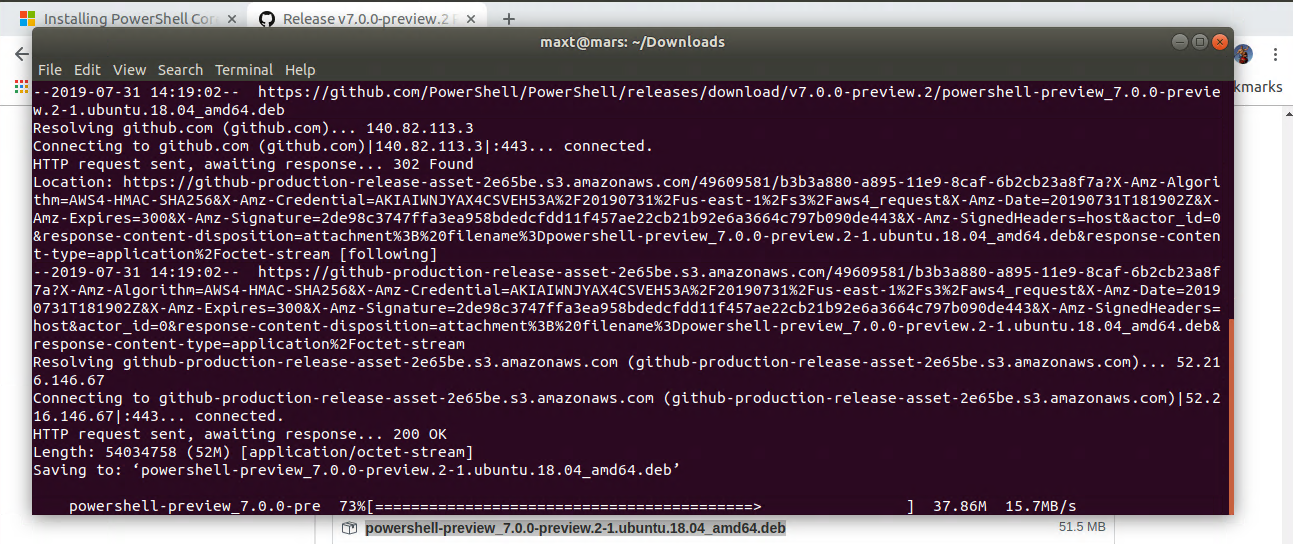
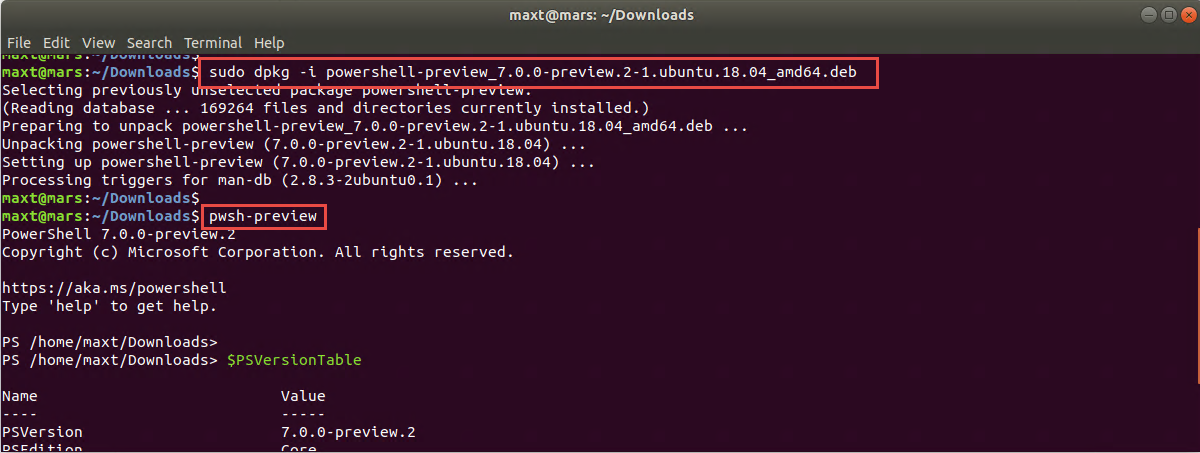
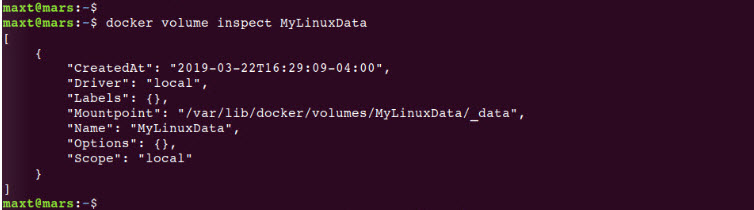
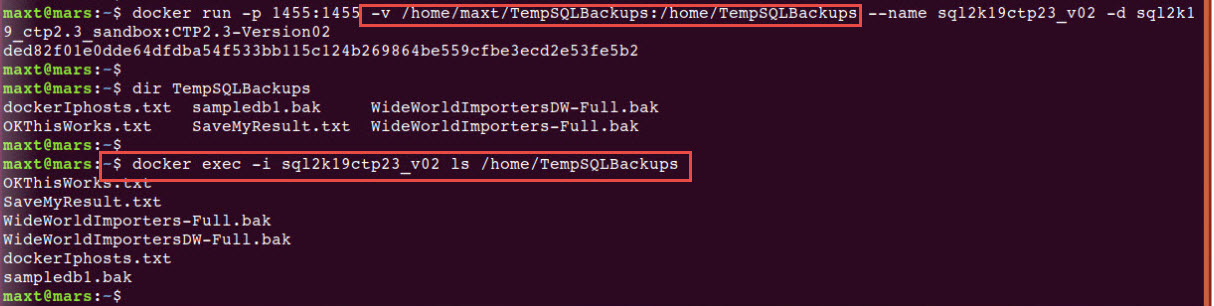
The purpose of this blog post is to show how to setup Docker Community Edition in a Windows 10 with VMware Workstation to be use in Windows Subsystem for Windows (WSL).
There are a few blog post that helped me figure out what’s needed to get this to work and I’ll be sharing these links at the end of this post.
My current environment
My current environment consist of the following components:
- Windows 10 Build 17763
- VMware Workstation Pro 12
- *Oracle Virtualbox 5.2
- WSL – Ubuntu 18.04
- SQL Server 2017 Developer Edition
- Windows PowerShell (v5.1.17763.316)
- PowerShell Core GA v6.3.1 (both Windows and Linux)
- PowerShell Core Preview v6.2.0-preview.4 (both Windows and Linux)
*Note: This is not the latest version of Virtualbox but it’s still supported.
Remember, the purpose of this environment is to build a “developer sandbox” that can allow me to learn and work with Docker containers.
What’s needed!
Because I’m using VMware Workstation instead of Hyper-V, there are a few things need to be in place to make this work. Windows 10 need to have the following:
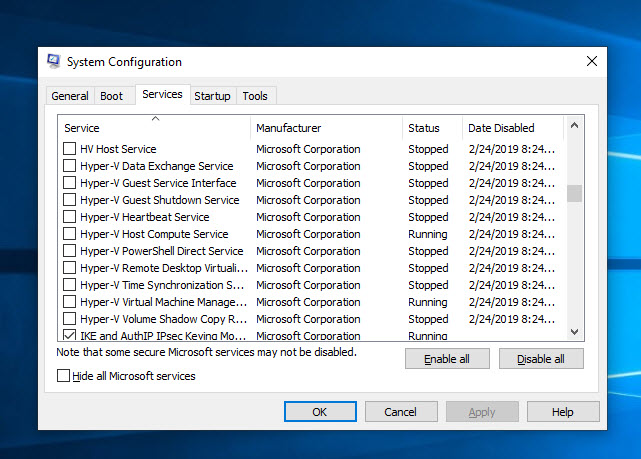
- All Hyper-V services need to be disable by using “System Configuration” tool.

- Install VMWare Workstation Pro. (https://www.vmware.com/products/workstation-pro.html)
- Install Oracle Virtualbox version 5.2. (https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Download_Old_Builds_5_2)
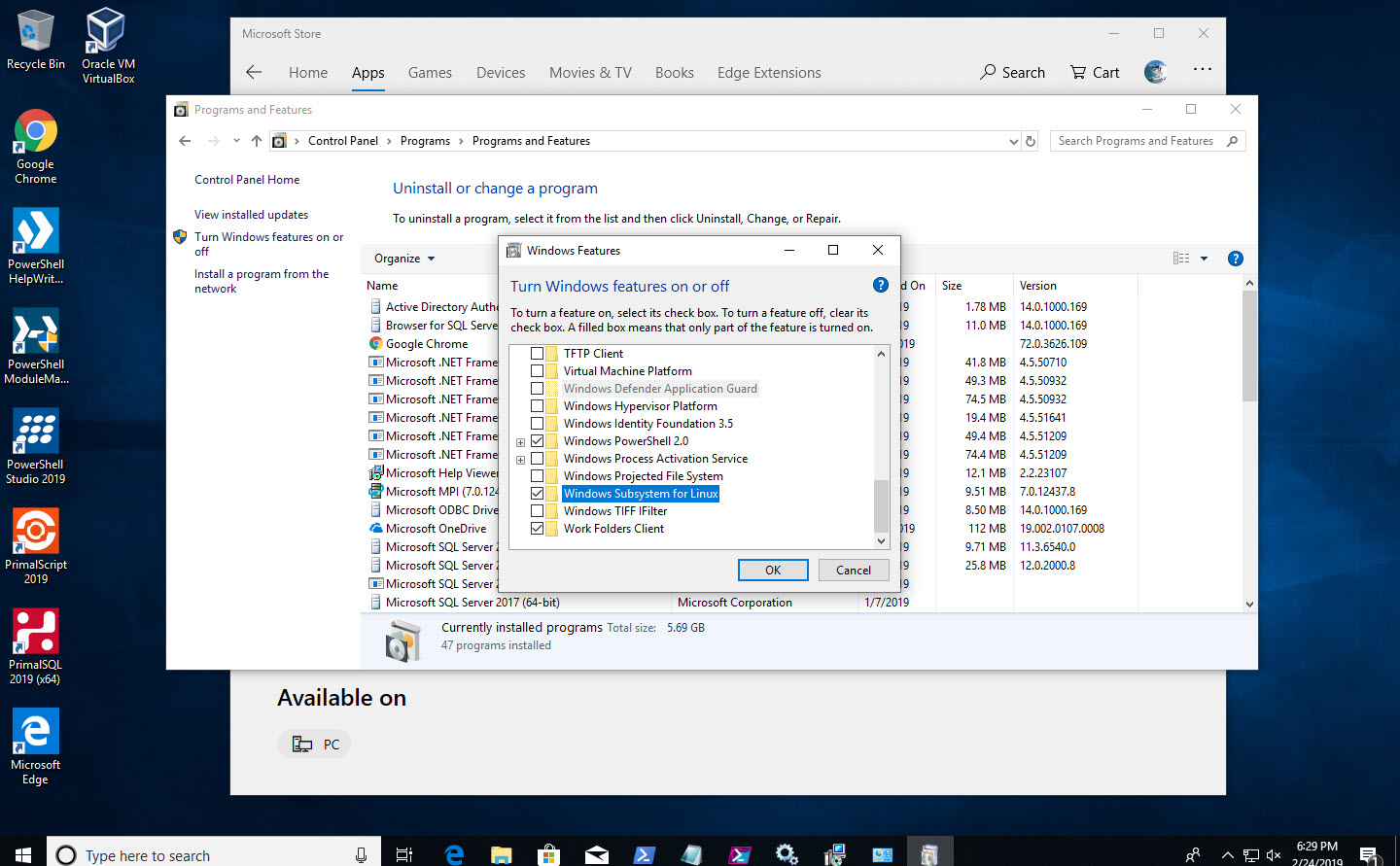
- Install from the Microsoft Store, WSL – Ubuntu 18.04.
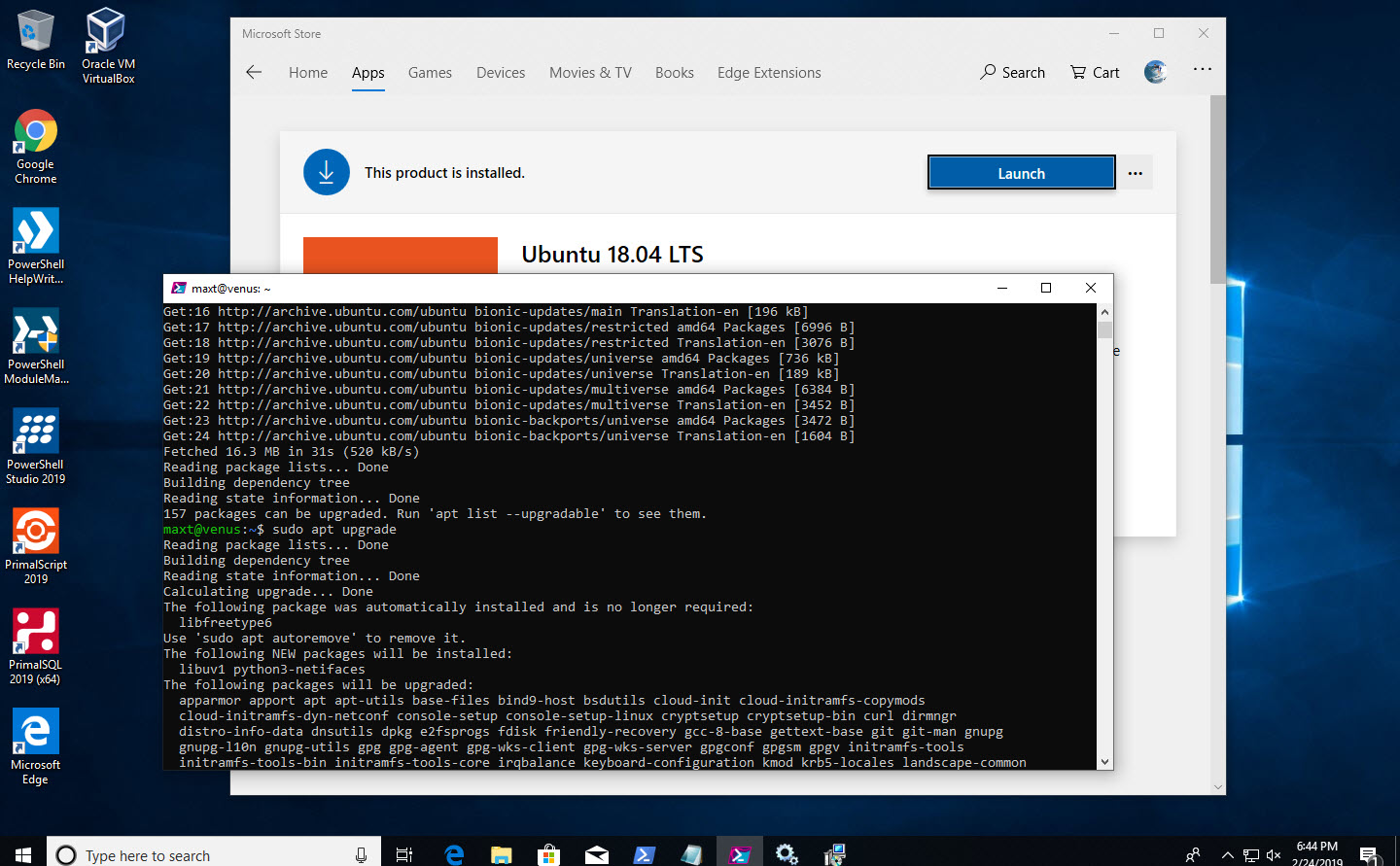
- And, make sure to run “sudo apt update” and “sudo apt upgrade” because images are not updated with latest components.
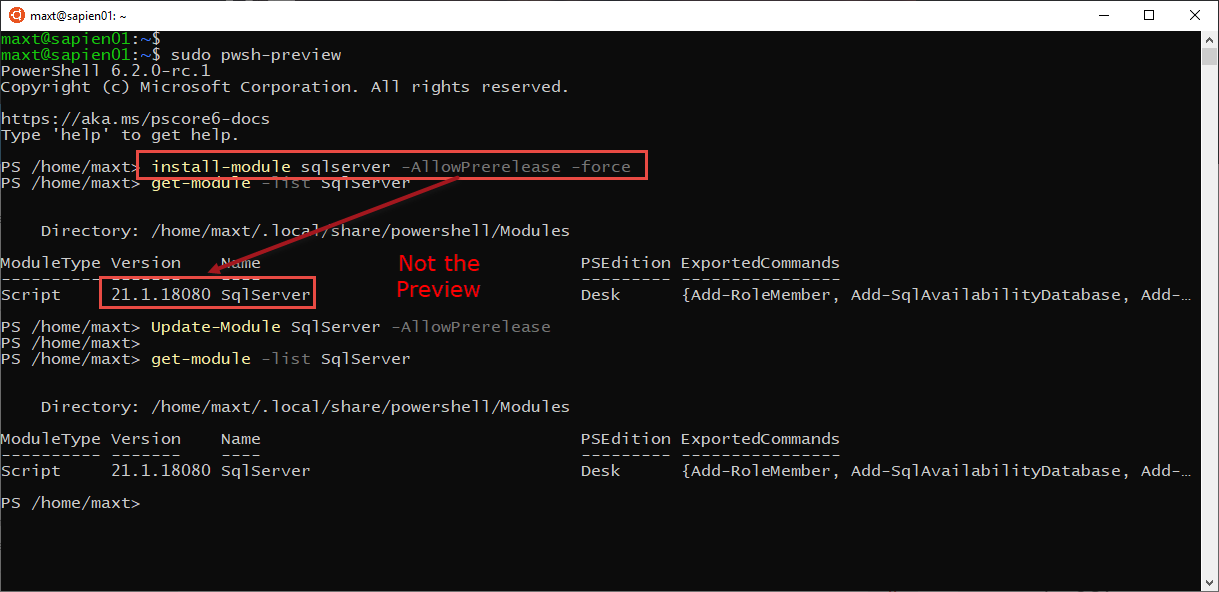
Installing PowerShell Components
Next, the following Docker components packages from Chocolatey need to be install using Windows PowerShell with administrator privileges:
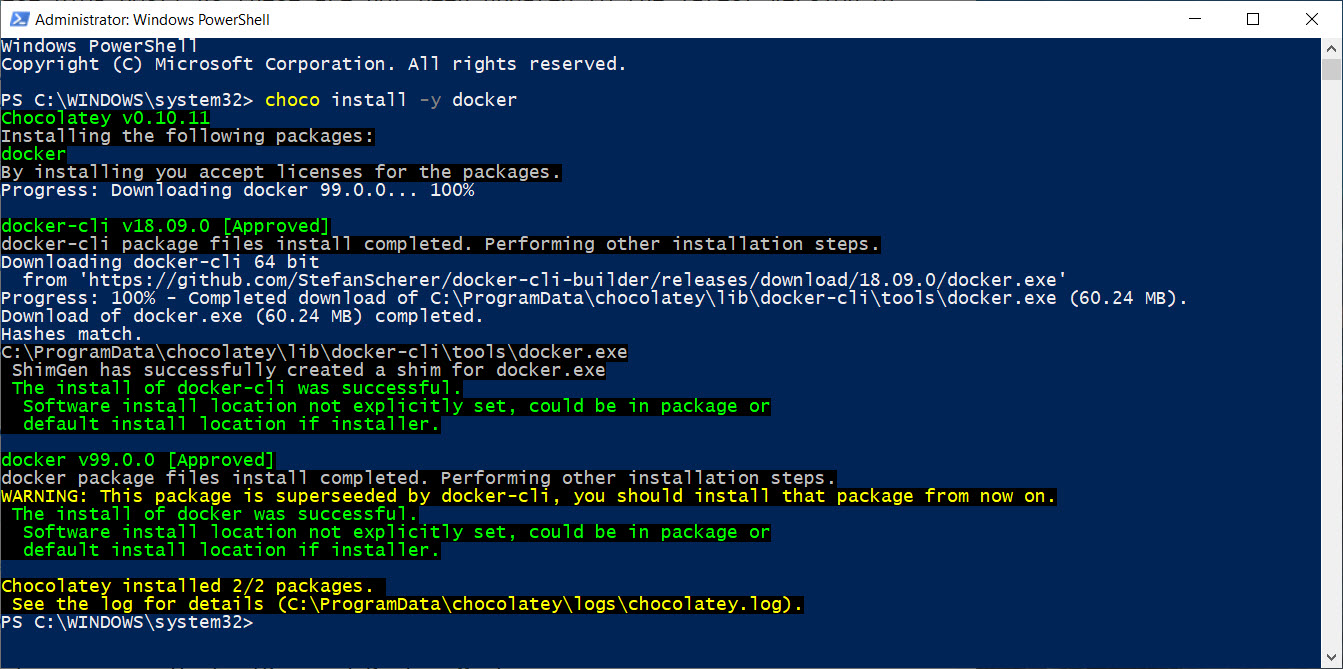
* Install docker
choco install -y docker
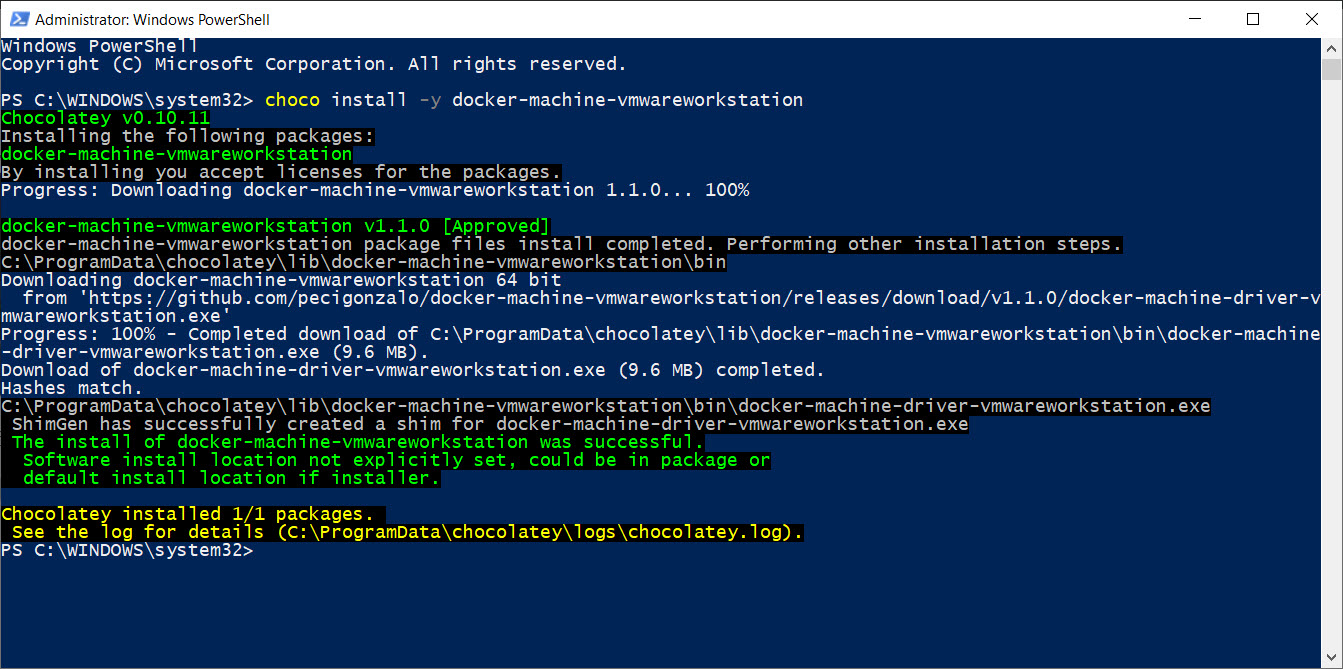
* Install docker-machine-vmwareworkstation
choco install -y docker-machine-vmwareworkstation
Getting WSL Ready for Docker
Now, open the “WSL – Ubuntu 18.04” Linux console and execute the following *commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade
*Note: You’ll need to run these two commands manually to keep your Linux distribution up-to-date.
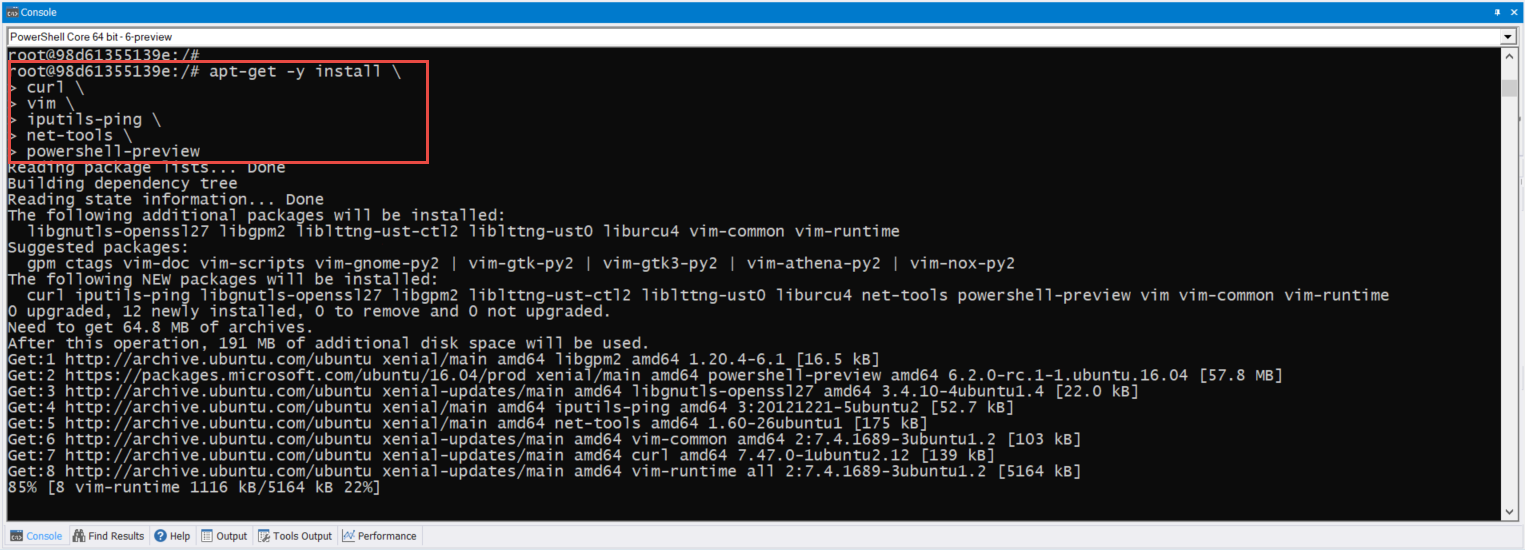
At this point, follow the Docker installation instructions for “Docker-CE for Ubuntu 18.04“. But, in a nutshell, here’s the shortcut:
sudo apt-get install \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg-agent \
software-properties-common
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
sudo add-apt-repository \
"deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) \
stable"
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt install docker-ce
sudo usermod -aG docker maxt
exit
At this point. make sure to reopen the WSL linux console.
Setup Docker-Machine in Windows
Back in Windows PowerShell, the next steps show the way to have Docker work in “WSL – Ubuntu 18.04“. Starting with Windows PowerShell console, execute the following commands:
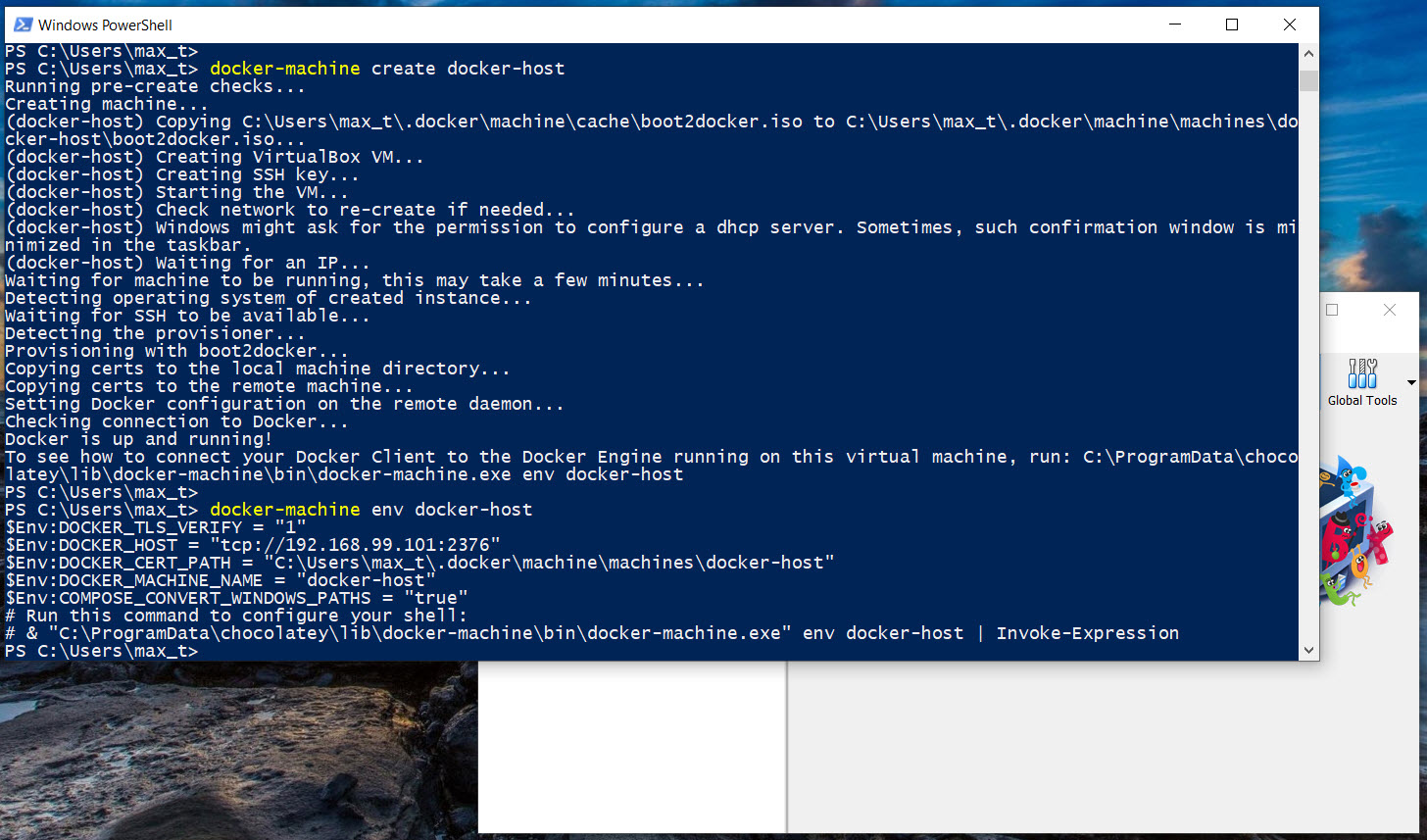
docker-machine --native-ssh create -d vmwareworkstation default
docker-machine create docker-host
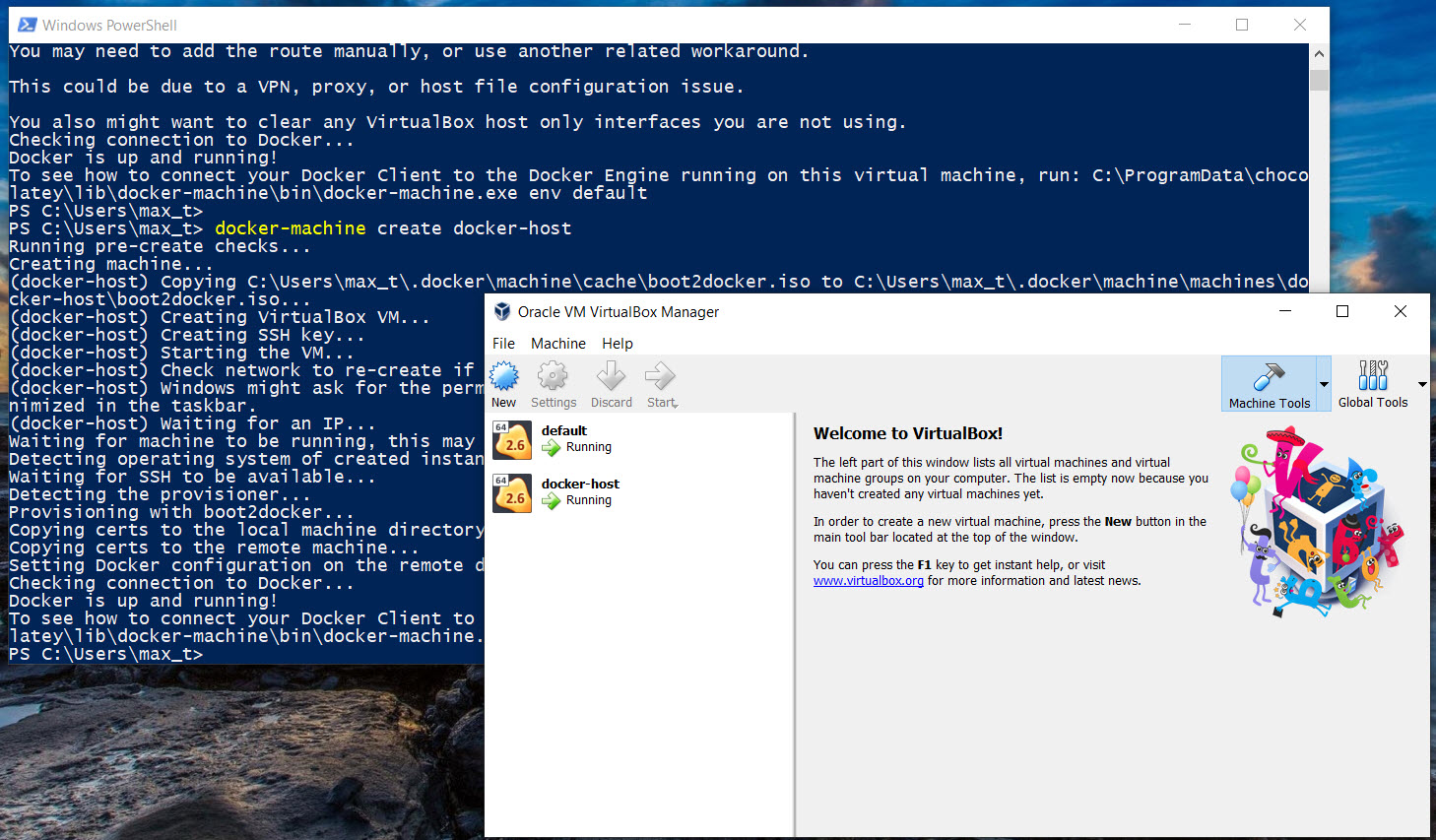
These commands should complete without any errors. At the same time, two virtual machines: “default” and “docker-host” will be created and running in *Virtualbox.
*Note: These two *NEED* to be running in order for docker to work with WSL. At the same time, both VMware Workstation and Virtualbox need to be installed or this will not work
To check that for the Docker-Machine environment(s) are working, use the following command:
docker-machine ls
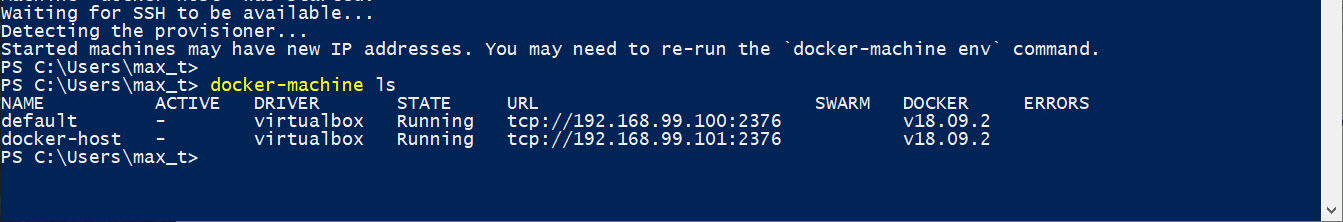
Next, execute the following command to write down “docker-host” environment results to be copied into the Linux user ~/.bashrc file.
docker-machine env docker-host
PS C:\WINDOWS\system32> docker-machine.exe env default
$Env:DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY = "1"
$Env:DOCKER_HOST = "tcp://192.168.220.xxx:2376"
$Env:DOCKER_CERT_PATH = "C:\Users\max_t\.docker\machine\machines\default"
$Env:DOCKER_MACHINE_NAME = "default"
$Env:COMPOSE_CONVERT_WINDOWS_PATHS = "true"
# Run this command to configure your shell:
# & "C:\ProgramData\chocolatey\lib\docker-machine\bin\docker-machine.exe" env default | Invoke-Expression
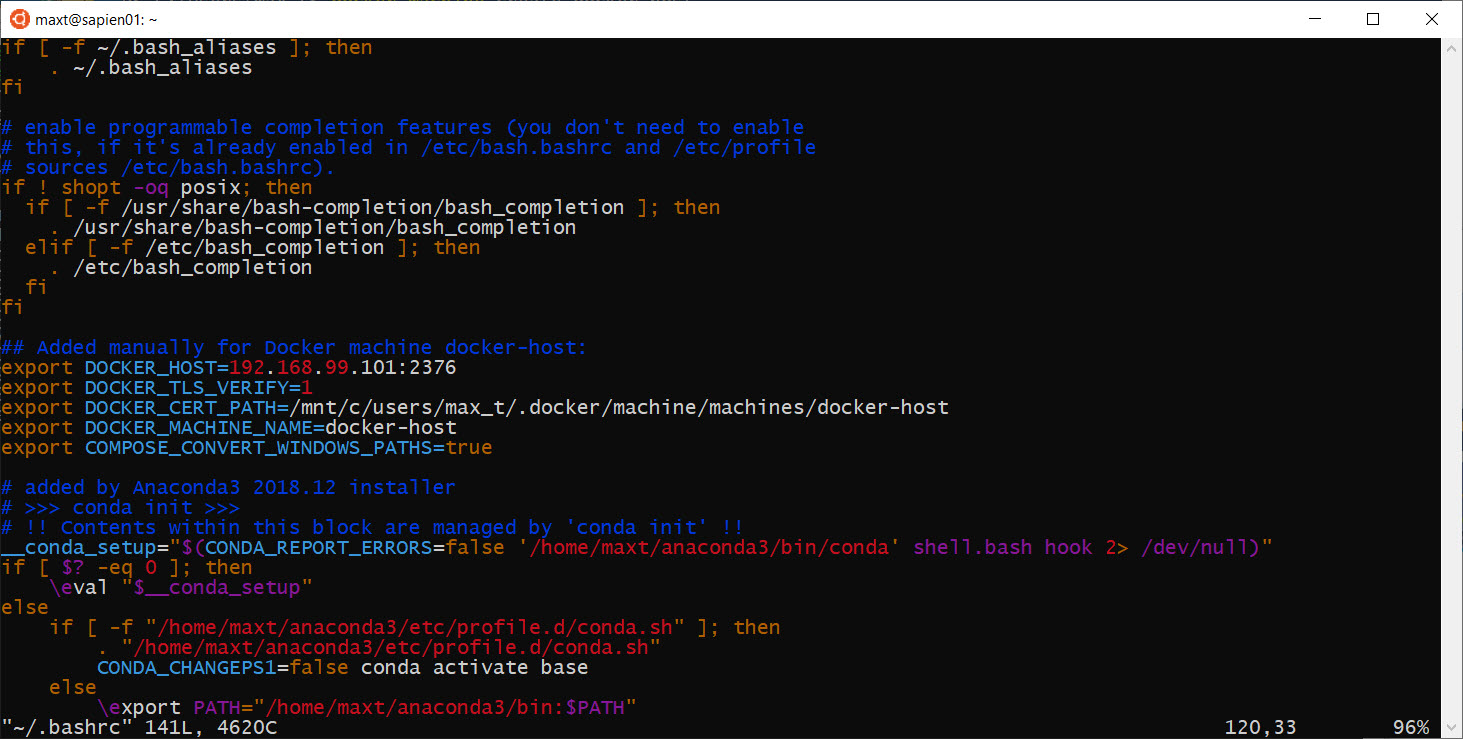
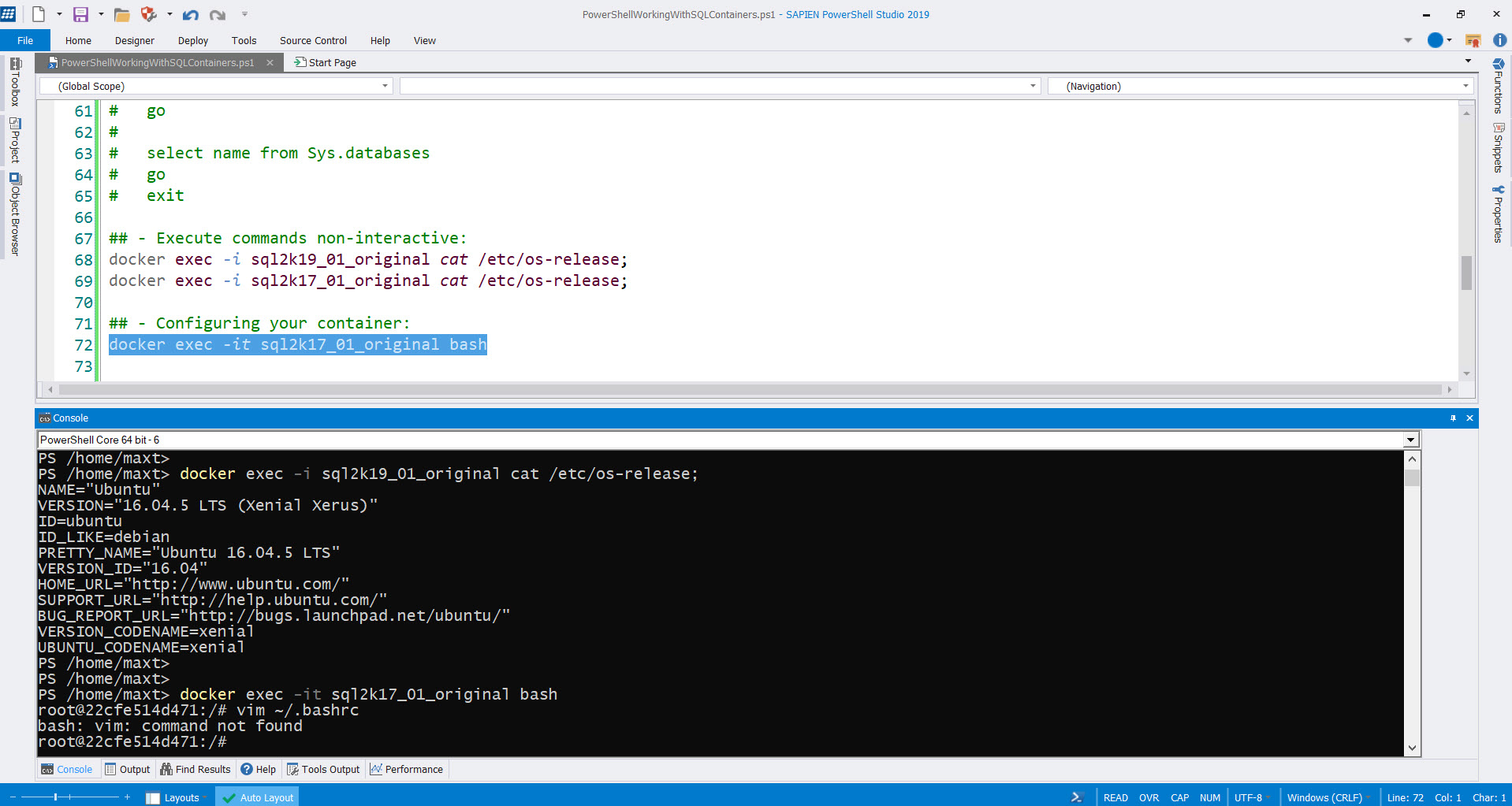
Open a “WSL – Ubuntu 18.04“ console to edit the user “~/.bashrc” file, to add the following Docker variables:
## Added manually for Docker machine docker-host:
export DOCKER_HOST=192.168.99.xxx:2376
export DOCKER_TLS_VERIFY=1
export DOCKER_CERT_PATH=/mnt/c/users/max_t/.docker/machine/machines/docker-host
export DOCKER_MACHINE_NAME=docker-host
export COMPOSE_CONVERT_WINDOWS_PATHS=true
sudo vim ~/.bashrc
Reopen the “WSL – Ubuntu 18.04“ console.
Testing Docker in WSL
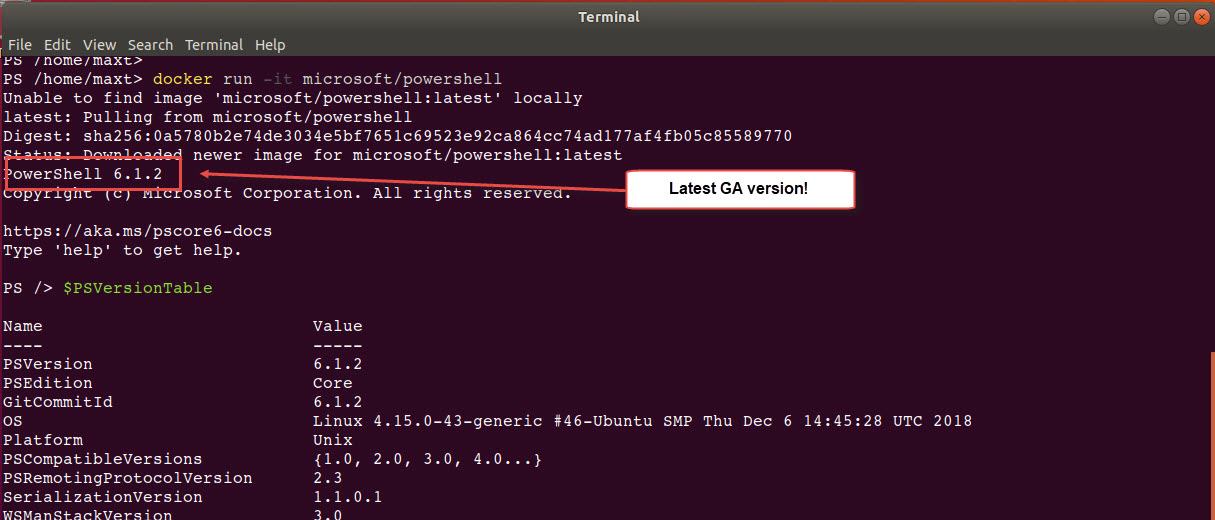
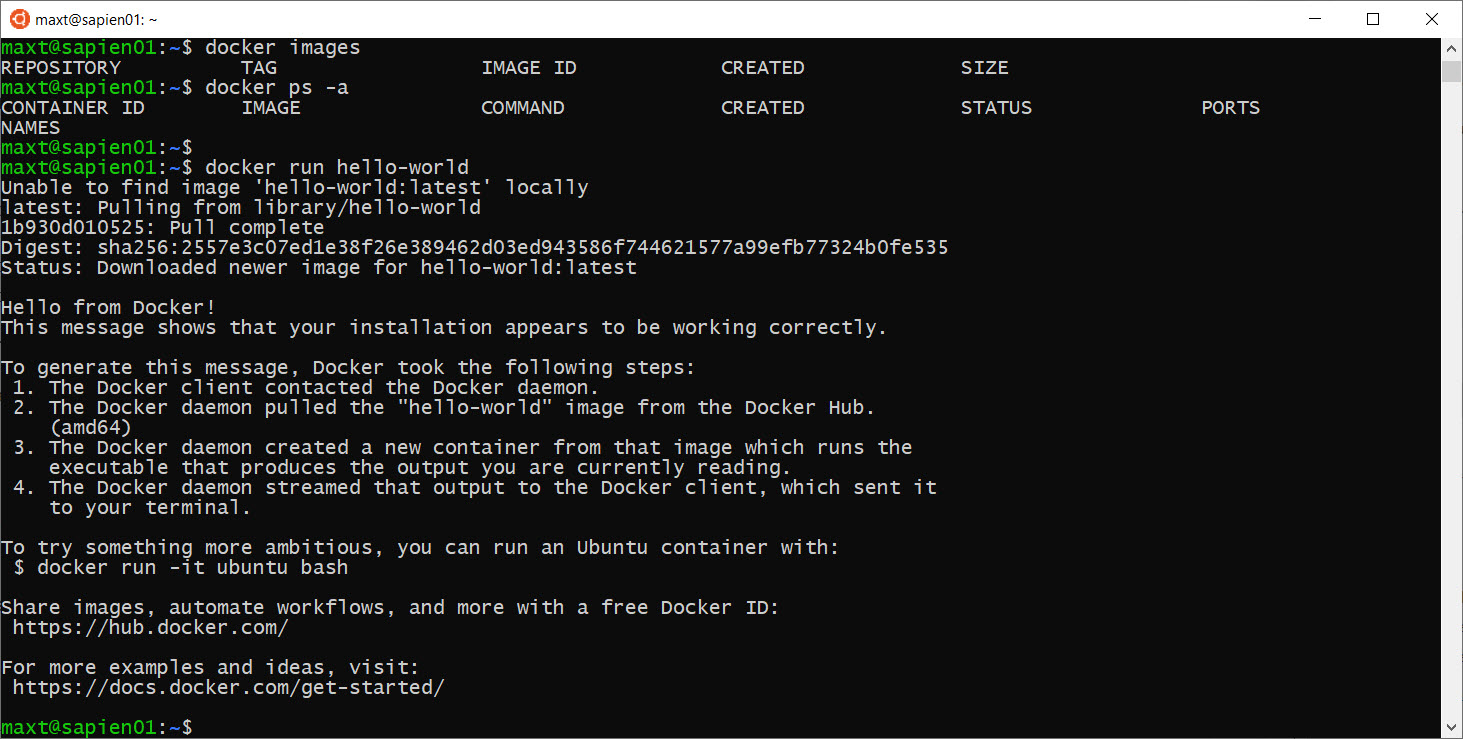
Now, I can test Docker in my “WSL – Ubuntu 18.04“ console session. Open PowerShell Core console, and execute the following command to run the Docker Hello-World demo:
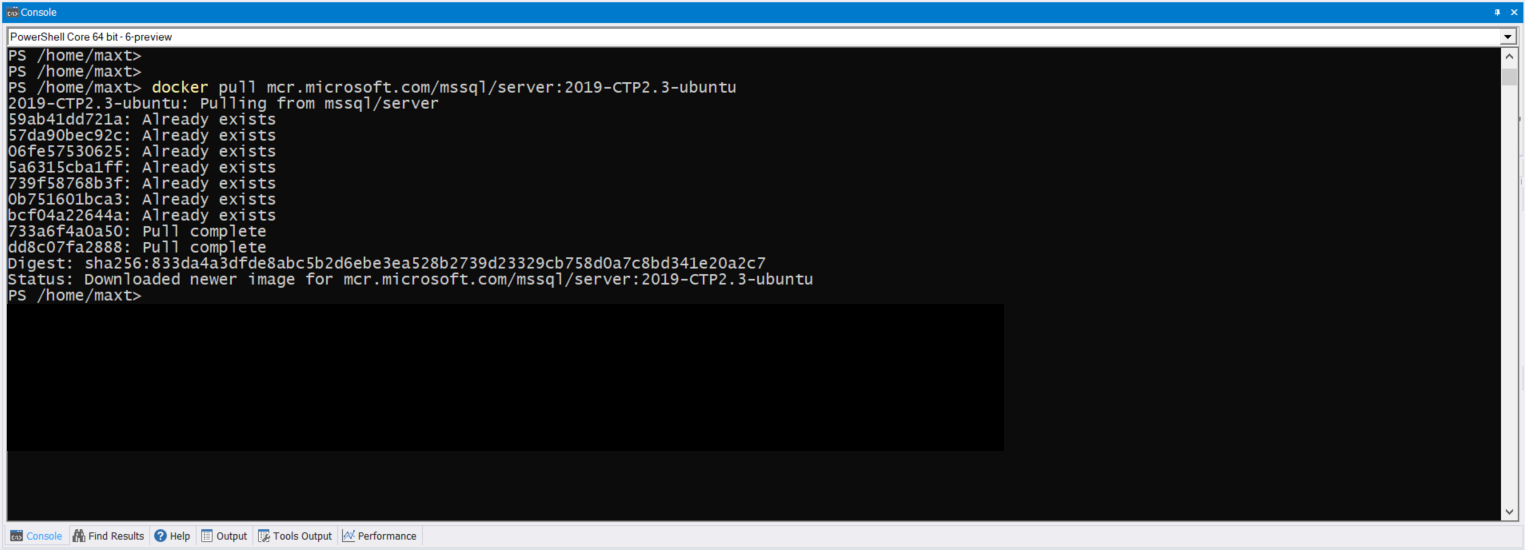
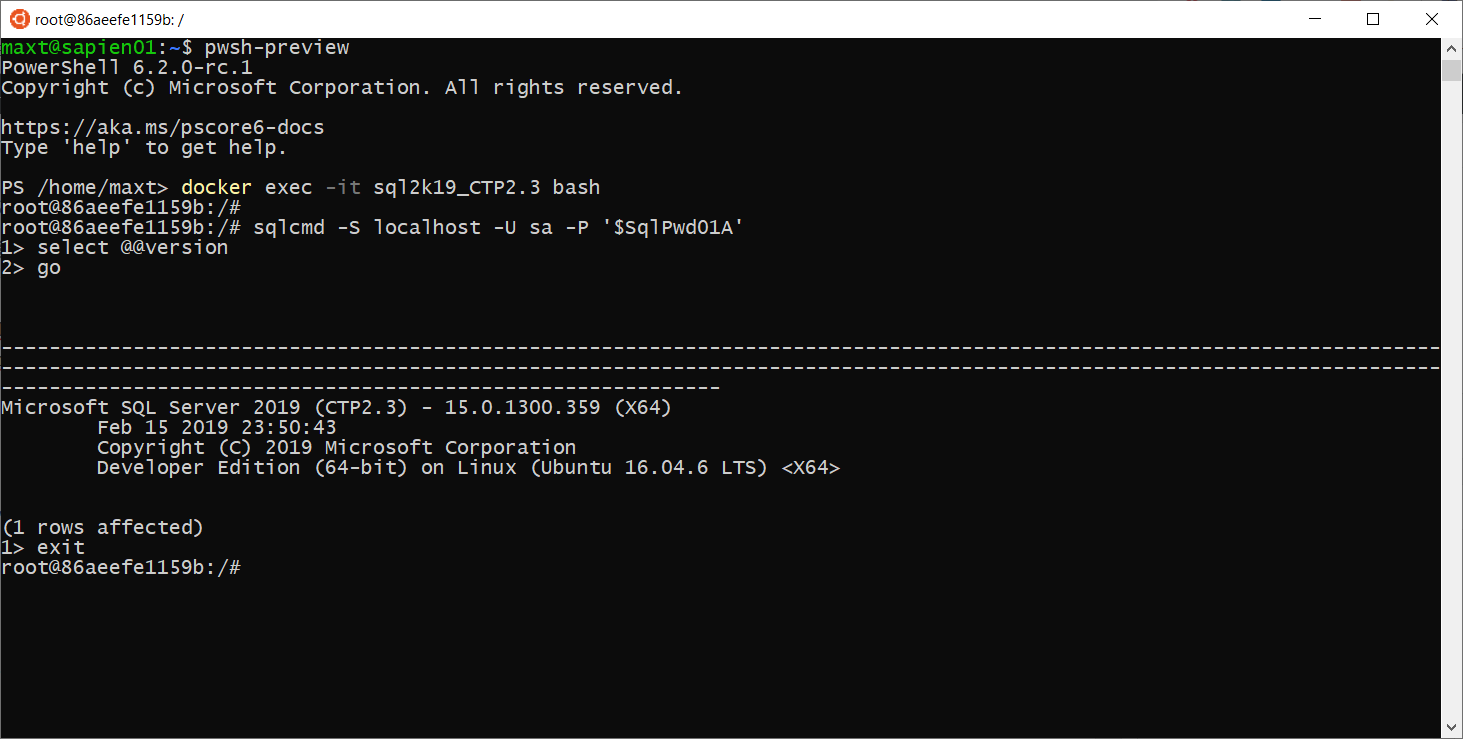
docker run Hello-World
This command download (or pull) the Docker image, then run the Hello-World container. If everything work as expected, then it will display the following text.
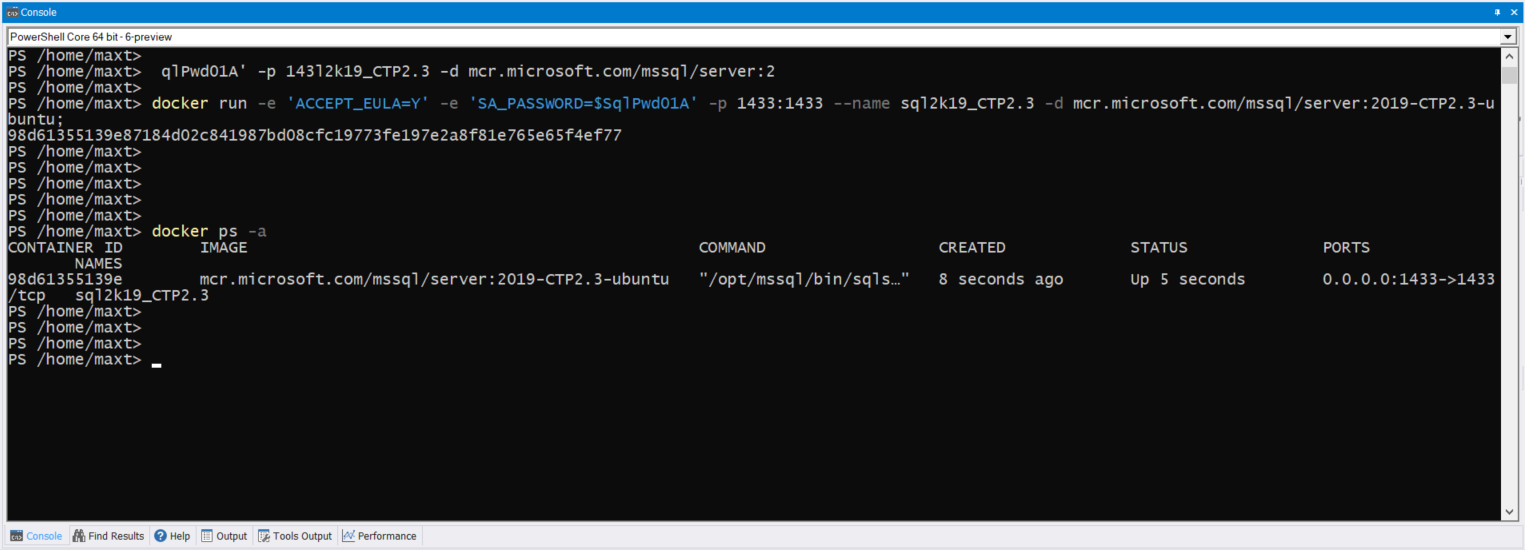
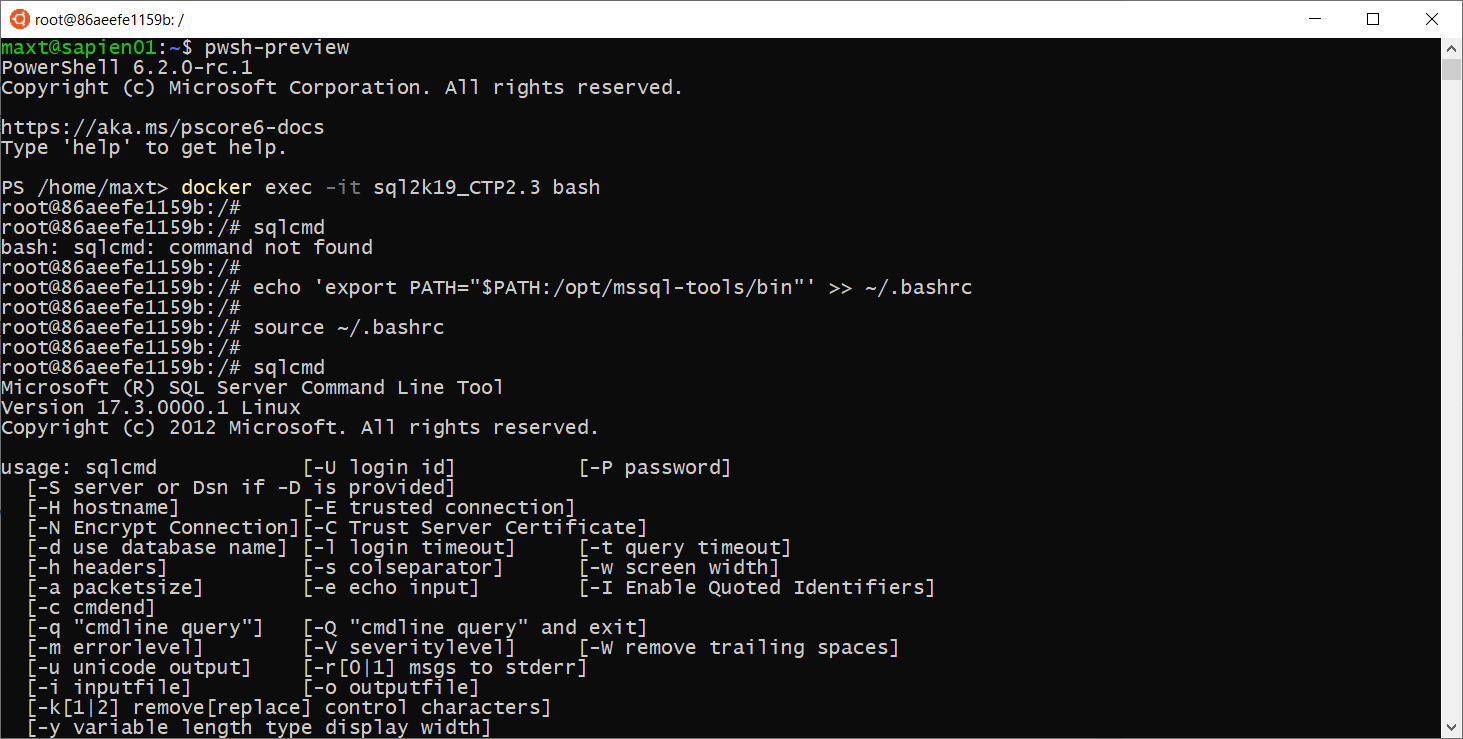
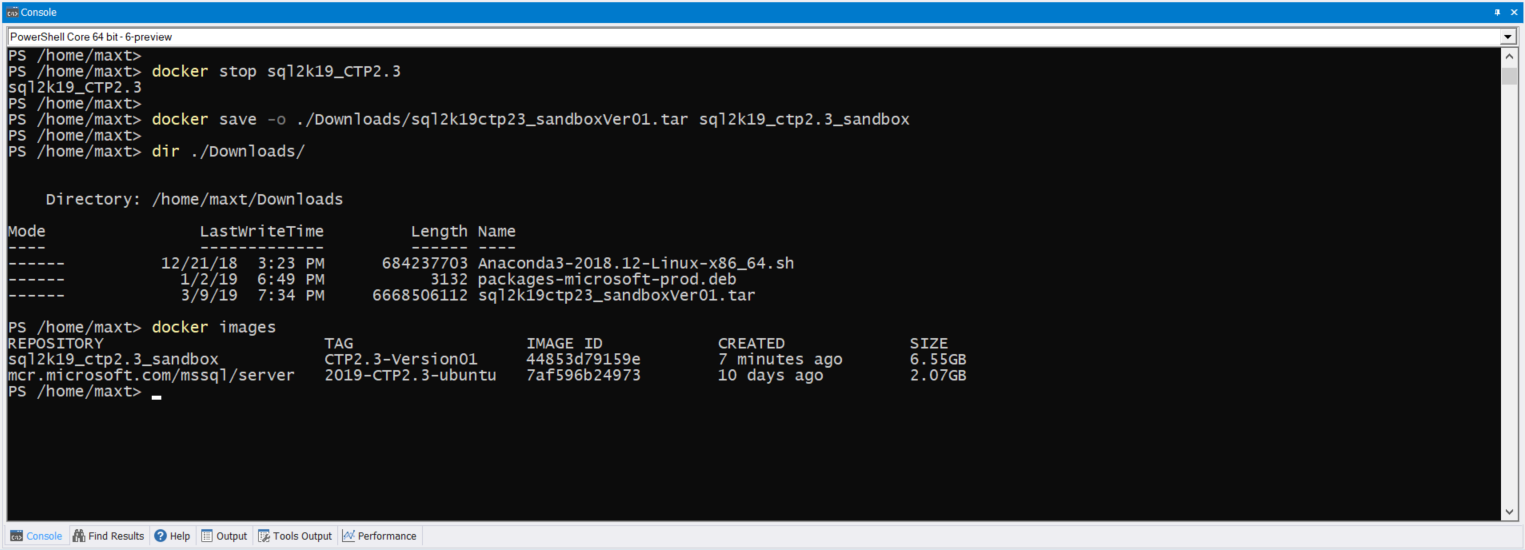
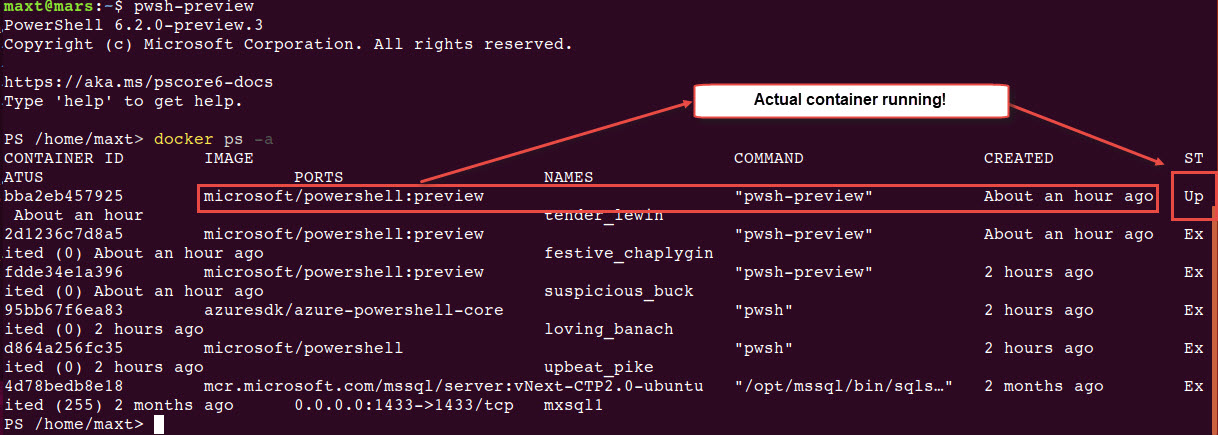
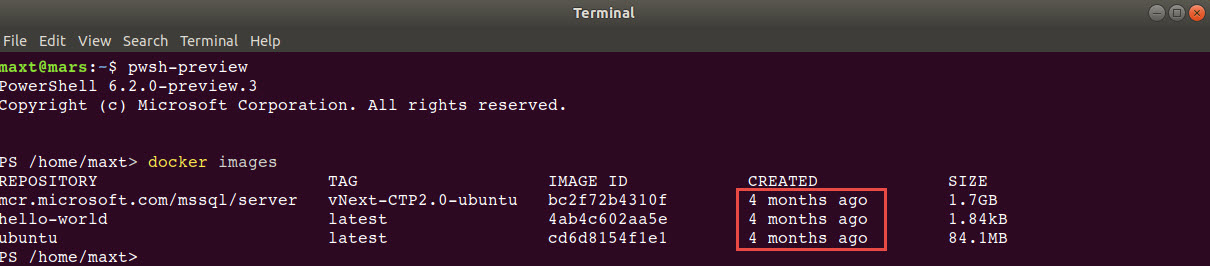
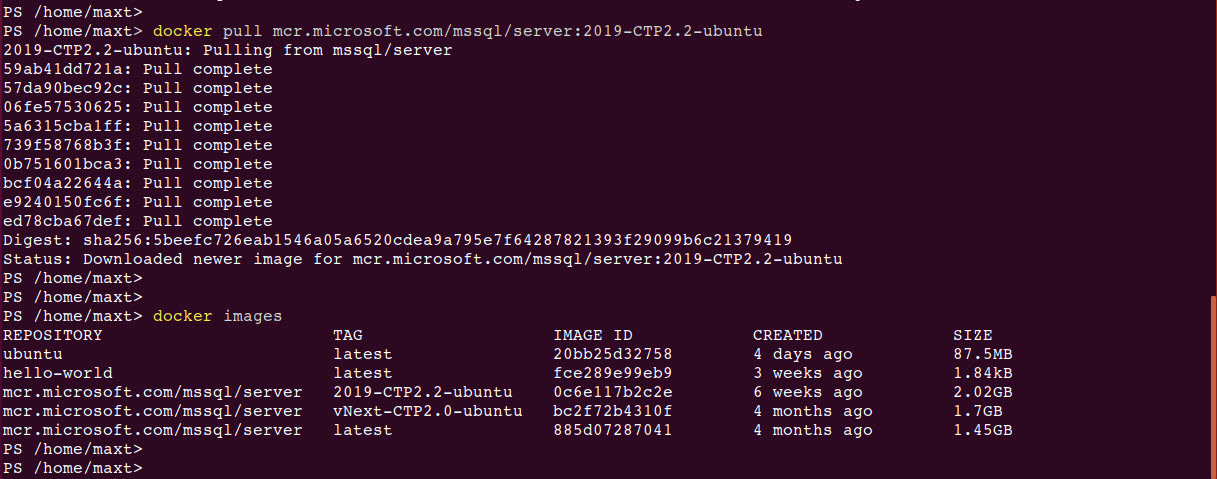
To check both Docker image(s) and/or container(s) in WSL , use the following commands: (Picture
# - Check for all pulled images in system:
docker images
# - Check the status of active containers:
docker ps -a
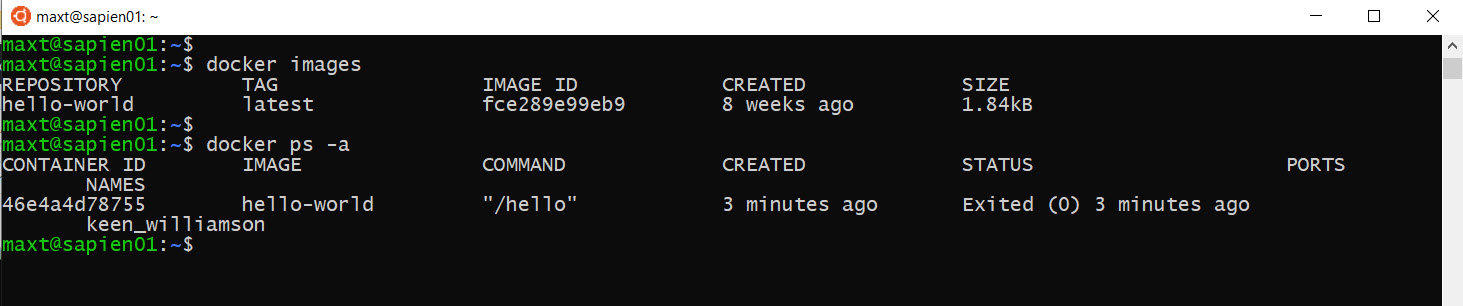
As you can see there no issues executing Docker command lines in Linux PowerShell Core.
To see the full list of docker command line help available click on the following link.
After all this is done! Docker working in my WSL environment.
Limitations
YES! There are limitations. This is a workaround on the issue of using Docker without Hyper-V. And, this will allow you to:
- Pull images
- Update containers
- Save images
In my environment, I found limitations working with Docker Network using WSL which can impact Windows Docker-Machine VM “docker-host” interface. This issue can force you to rebuild both VM interfaces: “default” and “docker-host“.
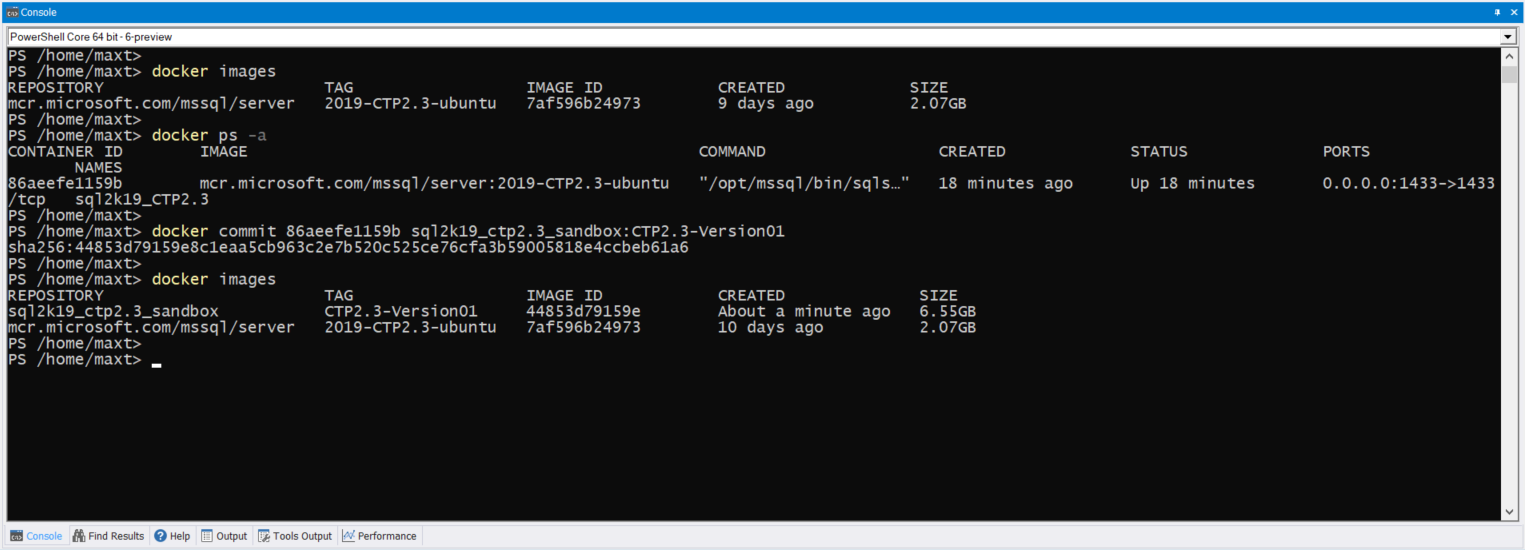
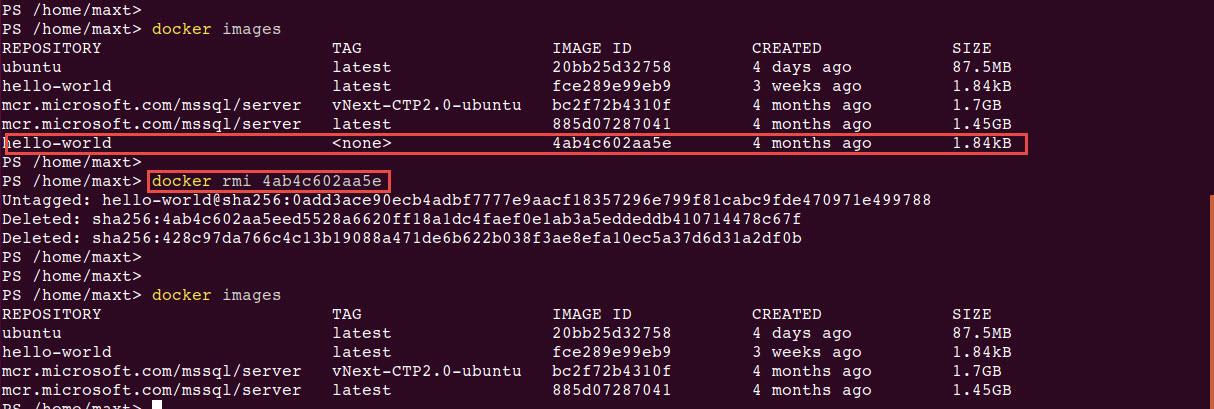
Make sure to learn how to commit, save, and reload Docker images. Don’t lose your changes!
So, if you have either VMware Workstation and/or Oracle Virtualbox, consider investing the time creating a Linux virtual machine and then install Docker CE.
Summary
We have accomplished setting up Docker containers in *Windows 10 “WSL – Ubuntu 18.04” using both Windows PowerShell and PowerShell Core in Linux. So, using Oracle Virtualbox v5.2 with VMware Workstation is a required component to make this work.
*Note: These post is meant for people to make Docker work in WSL Linux.
Also, if you’re familiar with PowerShell, Docker commands can execute without any issues. Now, I can use my favorite editor SAPIEN’s PowerShell Studio to build my automation scripts with docker commands.
What’s Next?
Try downloading other Docker images, like SQL Server 2017 and SQL Server 2019. This is the quickest way for providing a built solution using containers.
Learn about Docker Compose, and Kubernetes as these can be use in the Cloud environment as well.
Go and Explores the possibilities of provisioning solutions to your organization!
Resource links