On previous blog we have collect some data and built our .NET PowerShell object which is going to be loaded into our SQL Server.
In this final section we are completing the process of loading the data into SQL Server. We need to make sure we got our Database and table previously created and ready to receive our data.
For this process we’ll need to create 3 functions:
1. ConnectTo-SQLServer
2. Load-LogRecord
3. Process-PSObjectToSQL
Of course we could do everything in one long script file. But, by breaking out into it will make it much easier to handle and maintain.
In order to connect to SQL Server, we’ll be using straight SMO classes to load the data. Also, we’ll integrate some basic error catching using “try-catch” code block structure.
I’m keeping the functions in a basic level hardcoding some the PSObject variables instead of using parameter names. Keep in mind, the use of parameter name(s) in a function brings a lot flexibility and function reusability.
Function – ConnectTo-SQLServer
Using SMO with a few lines of code we connect to a SQL Server engine. Here’s the basic script code to will allow us to initiate a connection to SQL Server:
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
function ConnectTo-SQLServer
{
[CmdletBinding()]
param ()
## – Select SQLServer:
$global:SQLServerInstanceName = "MTRINIDADLT2";
$global:SQLServerDatabaseName = "LogEntries";
$global:logServerName = "tcgsvvm04";
�
## – Loading SMO .NET Assembly: (Required)
[system.reflection.assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("Microsoft.SQLServer.Smo") | Out-Null;
�
## – Connecting to SQL Server (Windows Authentication) and building you table object:
$global:SQLSvrObj = new-object(‘Microsoft.SqlServer.Management.Smo.Server’) $SQLServerInstanceName;
$global:SQLSvrObj.ConnectionContext.StatementTimeout = 0;
};
[/sourcecode]
You will notice the use the of “$global:variablename” with some of the variable objects created. This way we won’t loose the value stored in my PSObject(s) like “$global:SQLSvrObj” and have it available to other PowerShell function(s).
Function – Load-logRecord
This function show a Kind-Of template for using T-SQL insert statement to an existing table and at the same time subtitute the PSObject variable(s) constructing full qualify database table name. We construct the T-SQL Insert string and then to execute the query using SMO database *method “.ExecuteNonQuery($global:insertqry)”.
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
function Load-logRecord
{
CmdletBinding()]
Param ()
$global:insertQry = @"
INSERT INTO [$($global:SQLServerDatabaseName)].[dbo].[$($global:logServerName)_Log]
([Column1]
, [Column2]
, [Column3]
, [Column4]
, [Column5]
, [Column6]
, [Column7]
, [Column8]
, [Column9]
, [Column10]
, [Column11]
, [Column12]
, [Column13]
, [Column14]
, [Column15]
, [ServerName])
VALUES
( ‘$($global:l.Column1)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column2)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column3)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column4)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column5)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column6)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column7)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column8)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column9)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column10)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column11)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column12)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column13)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column14)’
, ‘$($global:l.Column15)’
, ‘$($global:LogServerName)’)
GO
"@;
 $global:SQLSvrObj.Databases["Master"].ExecuteNonQuery($global:insertQry);
};
[/sourcecode]
*Note: Keep in mind, by saving the PSObject variable with a $global: scope, you will access to its value after the function has been executed or the value will be dispose (null).
Function – Process-PSObjectToSQL
This is the heart of loading the data. Here we use both previous functions: 1. ConnectTo-SQLServer and
2. Load-LogRecord.
This a simple code block using the ForEach() block to read thru the PSObject variable to load the data into SQL Server. All accomplished with a few code block.
Now, here’s where we’ll include our error catching code block in case we encounter any data load issue during this process.
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
function Process-PSObjectToSQL
{
[CmdletBinding()]
param (
[array]$SQLDataObj
)
## Start process
Try
{
ConnectTo-SQLServer;
$global:cnt = 0
Write-Verbose "Start loading Data to SQL Server" -Verbose;
foreach ($global:l in $SQLDataObj)
{
Load-logRecord;
$global:cnt++;
}
}
catch
{
$global:ShowErr = @"
Insert SQL failed: Record #[ $($global:cnt) ]`n`r—–
Table: [$($global:SQLServerDatabaseName)].[dbo].[$($global:logServerName)_Log]`n`r—–
$($global:insertQry)`n`r—–`n`r$($error[0].Exception)
"@
[system.reflection.assembly]::LoadWithPartialName("System.Windows.Forms") | Out-Null;
[System.Windows.Forms.MessageBox]::Show("$global:ShowErr", "SQLInsertQry Exception") | Out-Null;
�
$errfound = $true
}
finally
{
## – Cleanup connection:�
$global:SQLSvrObj.ConnectionContext.Disconnect();
$global:SQLSvrObj = $null;
if ($errfound -eq $true)
{
Write-Verbose "Failure loading Data to SQL Server!" -Verbose;
$global:ShowErr | Out-File -FilePath c:\Temp\SQLDataLoadfailure.txt;
Invoke-Item c:\Temp\SQLDataLoadfailure.txt;
}else{
Write-Verbose "Completed loading Data to SQL Server" -Verbose;
}
}
};
[/sourcecode]
This function has a ParameterName $SQLDataObj. This will take the previously created $SQLData PSObject to be loaded to SQL Server.
In Error catching code block, the try{..} contains all the logic code to process the data. Then, the catch{..} has a custom string with enough information to trouble the issue the process may have encountered, such as: Fully qualified Database name, Insert Query T-SQL script, and the actual Exception error message.
At the end of the process, error or not, the finally{..} block will always execute the code. In this case, to disconnect and cleanup the connection to SQL Server.
Executing the process
After all the previous functions has been loaded, just type the following one-liner:
Process-PSObjectToSQL -SQLDataObj $SQLData;
This sample script code can serve as a startup Template to load data into SQL Server.
This sample SQL data load will fail. Here’s when the Try/Catch/Finally will work for you in trapping what went wrong. Adding the necessary code to provide that additional information to troubleshoot and fix the problem.
Be Creative! Check out the results.
- Data exception when inserting a record which was a transformation error in one of the fields.
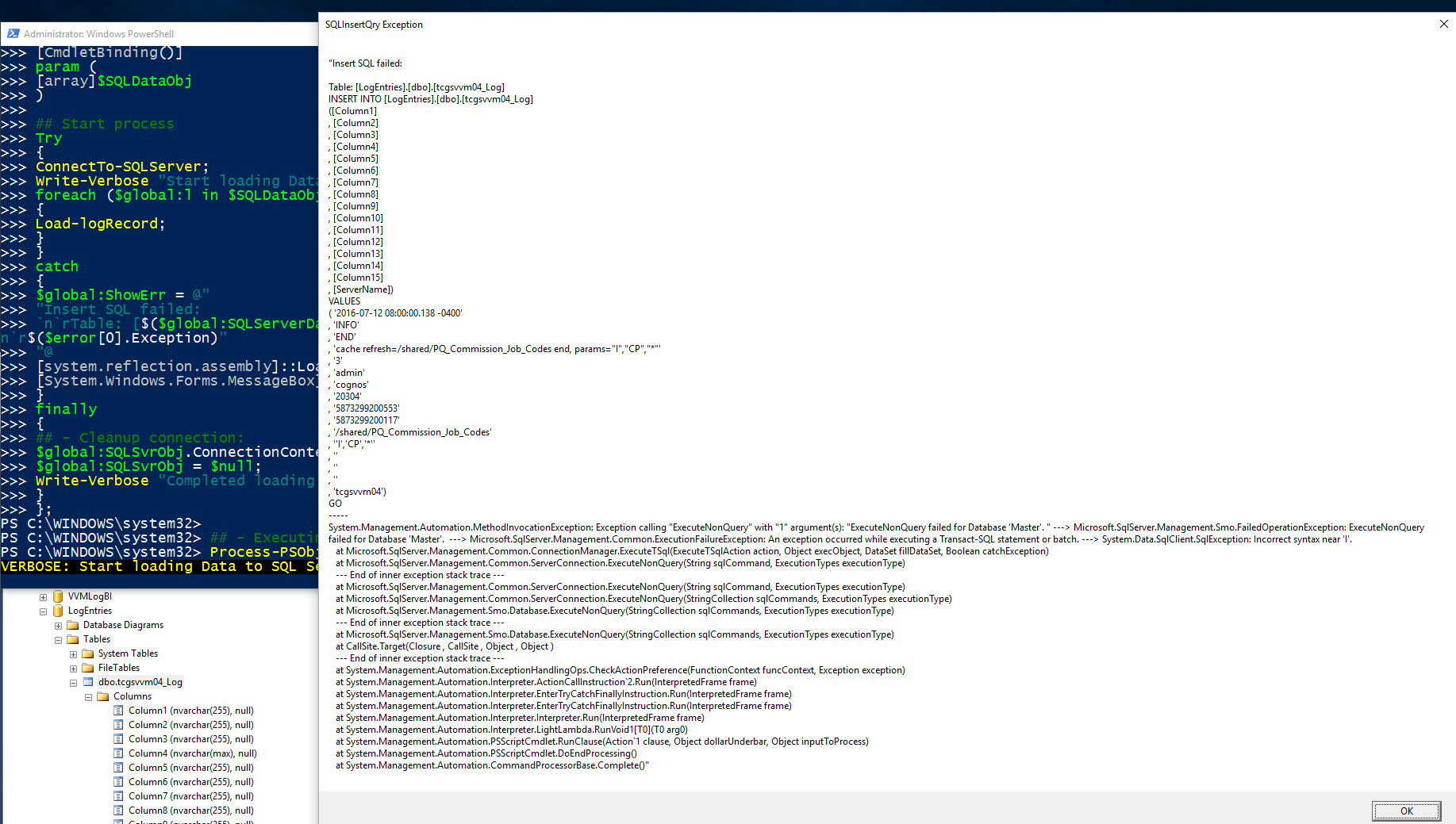
- Results generated from the data exception can be use to find what went wrong with this T-SQL insert script.
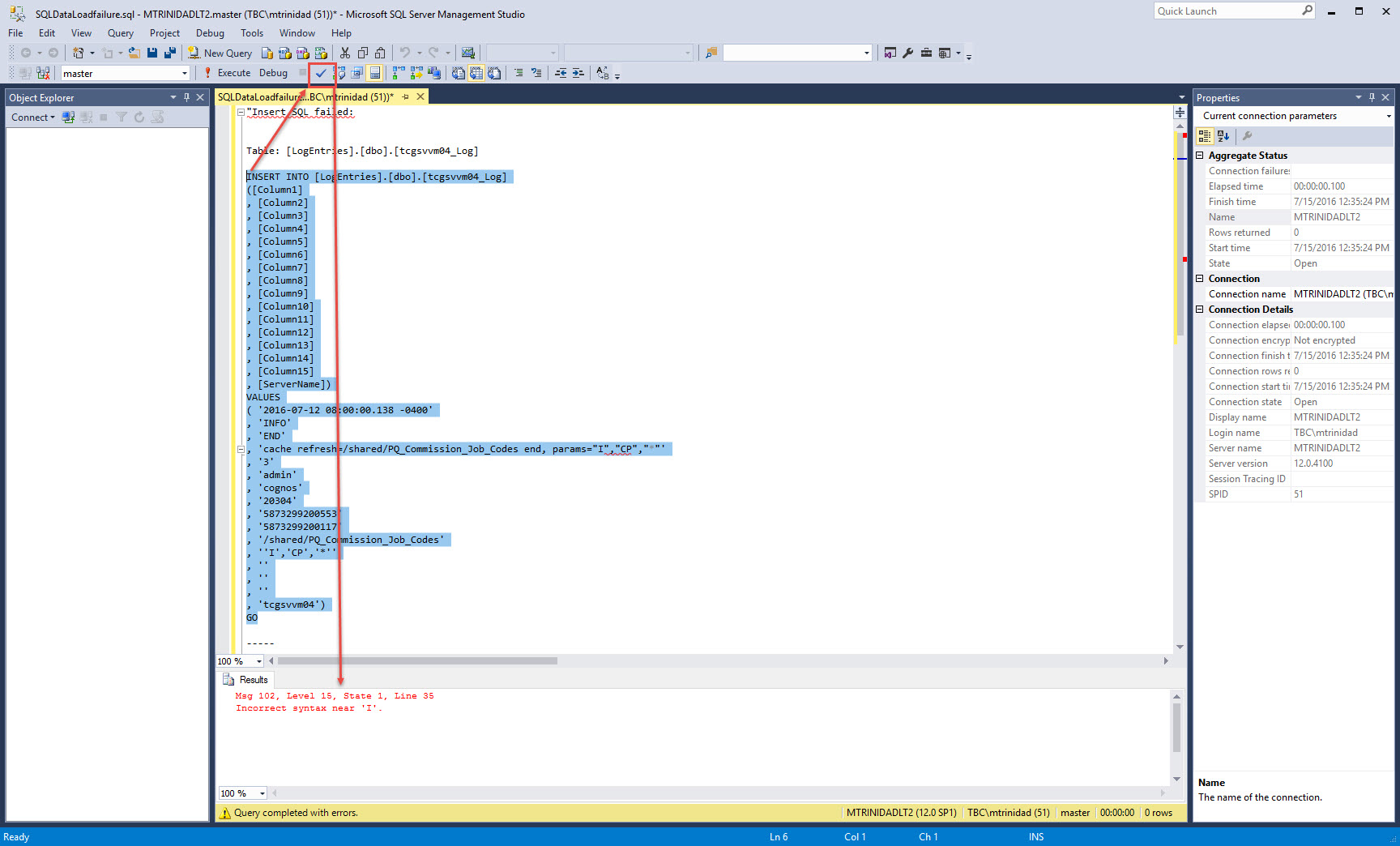
- Error exception code could generate an output file.
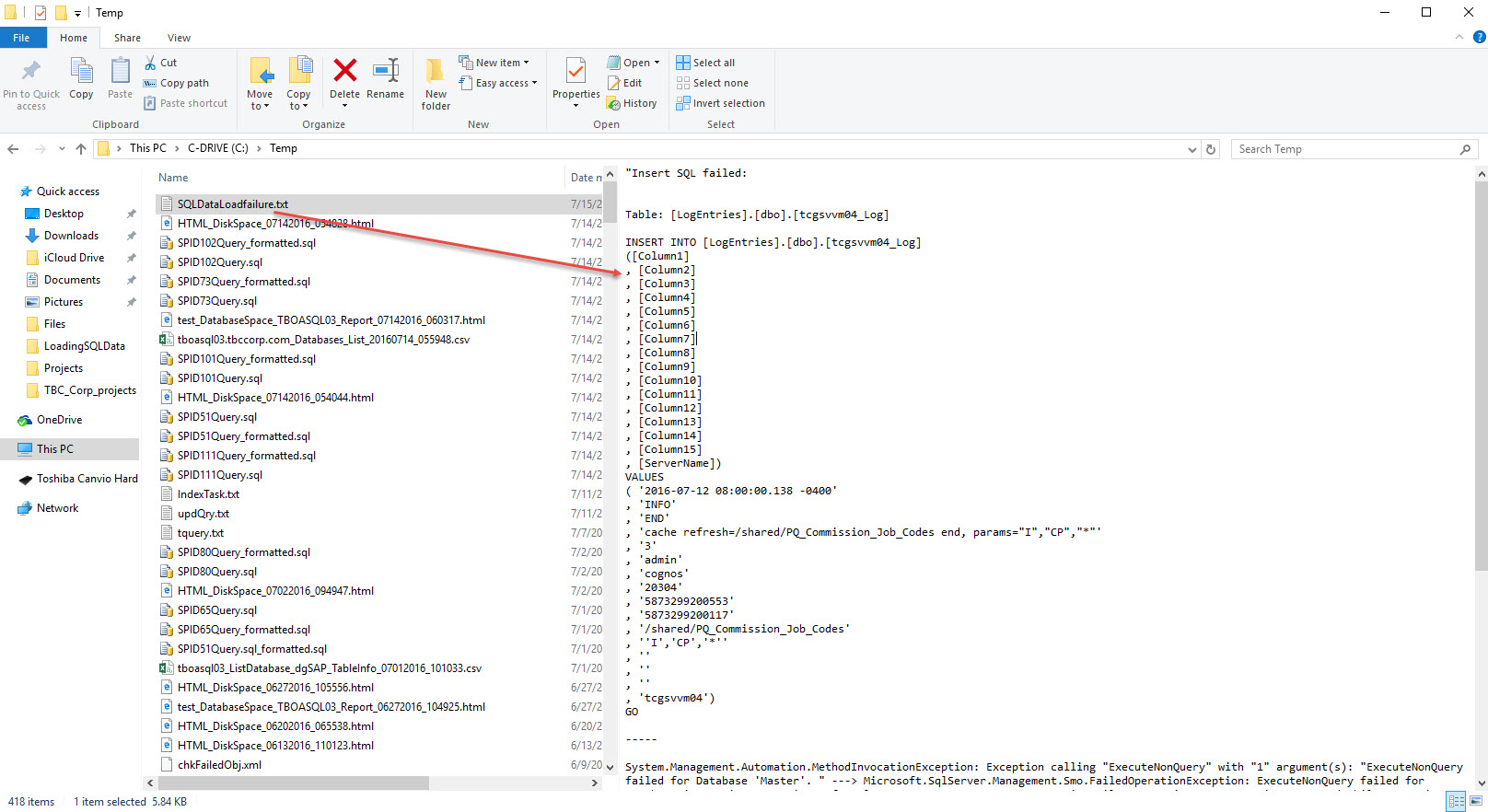
- Then, after fixing the issue, the data was completely loaded to SQL Server.
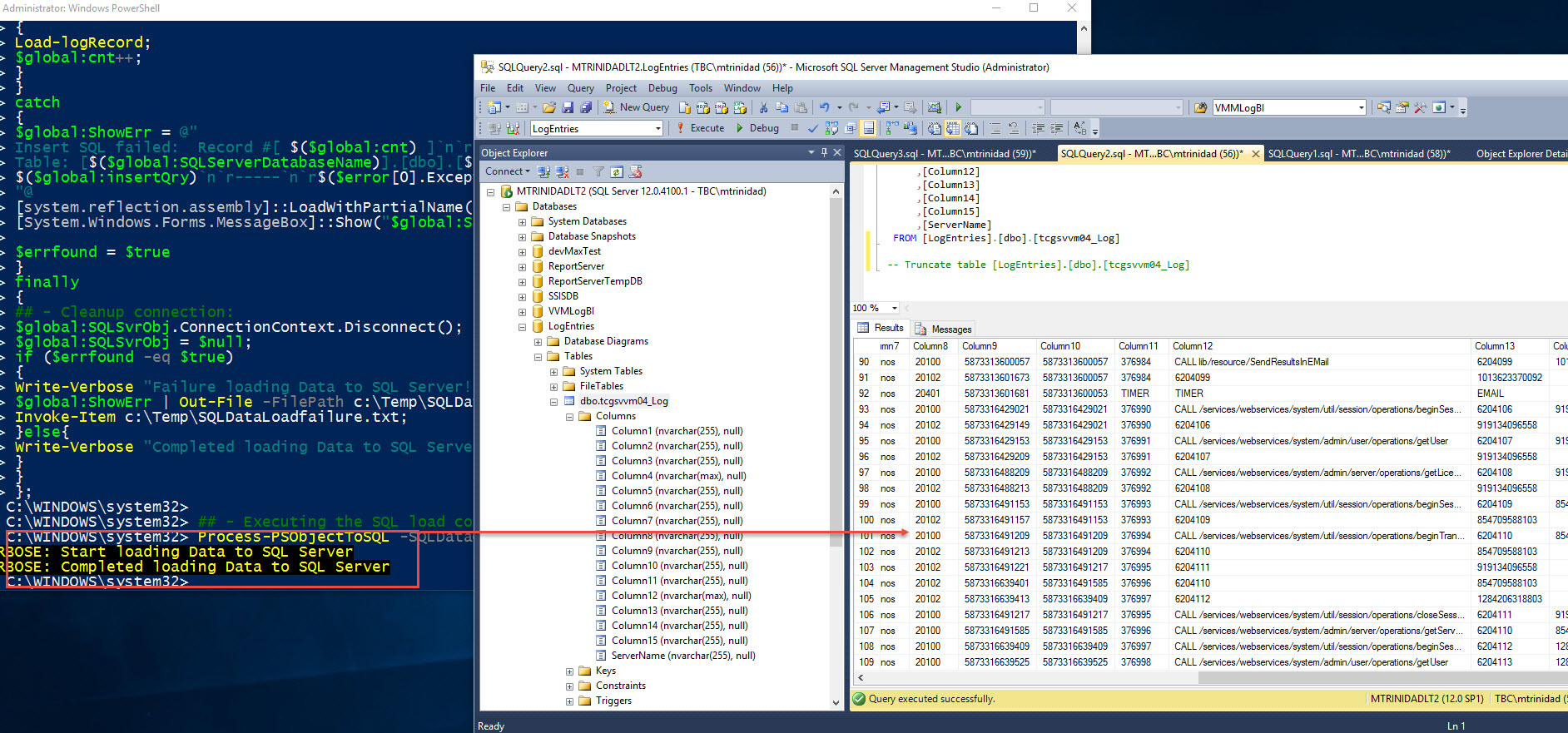
Happy PowerShell!