Thanks to our team member David Cobb has been able to help shape our new FLPSUG website. Please signup, become a member, and don’t miss our great speakers.
There’s more to come!
A little of everything about PowerShell!!!
Thanks to our team member David Cobb has been able to help shape our new FLPSUG website. Please signup, become a member, and don’t miss our great speakers.
There’s more to come!
Thank once again to the Palm Beach IT User Group for having my presenting live my session “PowerShell for the Administrator – All About The Language” on May 14th evening. http://itportalregulus.blogspot.com/
The group had the opportunity to see the evolution from a single one-liner command, to a script file, a function, and a brief taste to a module. Also, the scripts supplied has an abundant of code snippets that can be reused.
Also, giving example of reusing and modifying a community script (Thx, Jefferey Hicks for his contributions) so you can make it your own.
Here’s some reference links: http://jdhitsolutions.com/blog/2012/02/create-html-bar-charts-from-powershell/ and http://jdhitsolutions.com/blog/2011/12/friday-fun-drive-usage-console-graph/
Special Thanks to Sapien Technology for providing some books to giveaway and to Plurasight for the free one month online subscription.
Here’s the end result. A function that check the machine disk space, build an HTML file with a graph and send an email thru your live.com SMTP server.
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
function Get-DiskUsageHTMLGraph{
Param(
[array] $ComputerNames,
[string] $ReportPath = "c:\Temp\HTML_DiskSpace.html",
[boolean] $ViewReport,
[boolean] $SendEmail,
[Array] $SendTo
)
## – Set variable (no function):
$htmlTitle=’Server Drive(s) Report’
## – Configuring the HTML CSS Style sheet for the HTML code: (#FFFFCC)
## – When using Here-String/Splatting you must begin in the first position.
## – The use of Tab is invalid.
$head = @"
$($htmlTitle)
"@
## – Define the HTML Fragments as an Array type, add the header and title object:
[Array] $HTMLfragments = $null; $HTMLfragments += $head;
$HTMLfragments+="</pre>
<h1>Server Disk Space</h1>
<pre>
";
## – Build WMI Disk information object and group results by ComputerNames:
$SystemNames = get-wmiobject -Class Win32_logicaldisk -computer $ComputerNames `
| Group-Object -Property SystemName;
## – This is the graph character code:
[string] $gCode = [char] 9608;
## – Loop through each computer object found and create html fragments:
ForEach ($System in $SystemNames)
{
## – Get the System name:
$HTMLfragments+="</pre>
<h2>$($System.Name)</h2>
<pre>
"
## – Create an html fragment for each system found:
$html = $System.group `
| Where-Object {$_.DriveType -notmatch ‘5|2′} | Sort-Object -Property Name `
| Select-Object `
SystemName, @{Label = "DriveID";Expression={$_.Name}}, `
VolumeName, FileSystem, DriveType, `
@{Label="DiskSizeGB";Expression={"{0:N}" -f ($_.Size/1GB) -as [float]}}, `
@{Label="FreeSpaceGB";Expression={"{0:N}" -f ($_.FreeSpace/1GB) -as [float]}}, `
@{Label="PercFree";Expression={"{0:N}" -f ($_.FreeSpace/$_.Size*100) -as [float]}}, `
@{Label="Low if(($_.FreeSpace/$_.Size*100) -le ’15’) `
{ `
"- Critical -"; `
} `
Else `
{ `
$null; `
}; `
}}, `
@{Name="";Expression={ `
$UsedPer = (($_.Size – $_.Freespace)/$_.Size)*100; `
$UsedGraph = $gCode * ($UsedPer/2); `
$FreeGraph = $gCode * ((100-$UsedPer)/2); `
"xltFont color=Redxgt{0}xlt/FontxgtxltFont Color=Greenxgt{1}xlt/fontxgt" `
-f $usedGraph,$FreeGraph; `
}} | ConvertTo-Html -Fragment;
## – Replacing replace the tag place holders: (Jefferey’s hack at work)
$html=$html -replace ‘xlt’,’
## – Add the Disk information results to the HTML fragment:
$HTMLfragments+=$html;
## – Insert a line break for each computer it find:
$HTMLfragments+="
";
}
## – Add a footer to HTML code:
$footer=("
<em>Report run {0} by {1}\{2}<em>" -f (Get-Date -displayhint date),$env:userdomain,$env:username)
$HTMLfragments+=$footer
## – Write HTML code to a file on disk:
ConvertTo-Html -head $head -body $HTMLfragments | Out-File $ReportPath;
if($ViewReport -eq $true)
{
ii $ReportPath;
}
if($SendEmail -eq $true)
{
## – Setting the information for hotmail:
$MyEmailAcct = "UserX@live.com";
$MyPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString ‘$myPassword!’ -AsPlainText -Force;
$MyCredentials = new-object -typename System.Management.Automation.PSCredential -argumentlist $MyEmailAcct,$MyPassword
[Array] $emaillist = @(‘User1@gmail.com’,’UserX@live.com’);
## – OR, send it as a body message in the email:
$GetError = $null;
Send-MailMessage `
-From ‘MySysAdmin-DoNotReply@MySysAdmin.com’ `
-To $SendTo `
-Subject "Diskspace Information for the date – $((Get-Date).ToString("MMddyyyy, HH:MM"))" `
-BodyAsHtml ([string] (ConvertTo-Html -head $head -body $HTMLfragments)) `
-SmtpServer ‘smtp.live.com’ `
-Credential $MyCredentials `
-UseSsl `
-Port 587 `
-ErrorAction SilentlyContinue `
-ErrorVariable GetError;
if($GetError -ne $null)
{
$date = (get-Date).ToString("MMddyyyy_HHMMss");
"Sender: $($getCred1.UserName) `r`n $GetError" | `
Out-File -FilePath "C:\Temp\log\emailerror_$date.txt";
};
};
};
[/sourcecode]
Sample results for email to live.com: 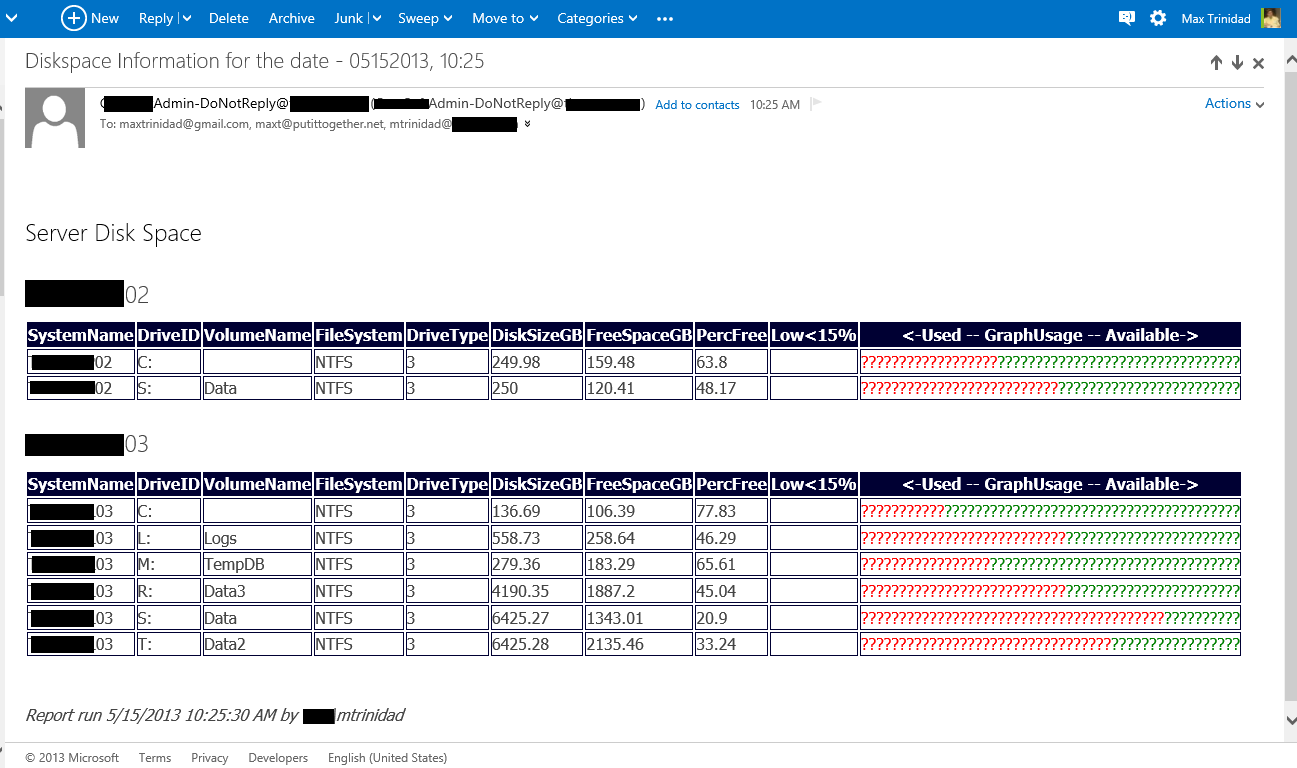
Sample Browser:
Here’s the zipped presentation link:
Take a look at my SQL Server SMO article “Using SQL Server Management Objects with PowerShell” in the “SQL Server Pro” April magazine is available now on the internet: http://www.sqlmag.com/article/windows-powershell/sql-server-managment-objects-powershell-144832
Here’s the “Getting Started with Windows 8 PowerShell” presentation plus one sample script to get you started.
Topic description: This is an introduction session on how to work with PowerShell 3.0 in Windows 8. I will cover find PowerShell, how to create your PowerShell shorcuts, updating PowerShell help documentation, and briefly covering the some of the enhancements in the ISE editor.
Click on the following link:
Thanks and keep participating with the IT Community!
It’s long overdue to our the Florida PowerShell User Group website to be update to something modern. So, we are doing some reconstruction and using DotNetNuke as our new CMS.
Please be patient! In the meantime you can connect to my blog page where I’m be posting the progress and new upcoming thing in our FLPSUG group.
Thank you for your support.
Saturday March 16th, 2013
First, Thanks to the organizers for having me speak about PowerShell and the gift they gave to all the speakers. Also, Thanks to all the sponsor’s and all whom attended my PowerShell sessions:
1. PowerShell Working with PSObjects.
2. PowerShell working with XML.
Here’s the zip file with both presentation and sample code for download:
Please don’t hesitate to contact me if you have any questions.
It was a pleasure to participate in this event.
Sometime is nice to find simple samples that can make life easy. Here’s a quick sample on how you can use this string manipulation to make it readable. Also, I included a way to dynamically create a PowerShell variable from an existing (it may be useful for someone) just as a proof-of-concept.
In this sample I’m going to create a T-SQL script and display it in my PowerShell console. First, let’s create some variables that will be use to replace some values in our string:
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
## – Dynamically creating a variable with a value:
$SubstituteVariable = "SQLDatabase";
New-Variable $SubstituteVariable -Value "Developer";
$Tablename = "AddressBook";
[/sourcecode]
The above code will create three PowerShell variable but we are end up using only the $SQLDatabase and the $Tablename in our T-SQL script.
The next few PowerShell code will show you a simple ways to initialize a string variable holding the T-SQL scripts.
1. One-liner sample – All acceptable except when using complex Multi-line T-SQL Scripts.
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
## [1] – Normal string one liner:
$SQLquery = "Select [firstname], [lastname] from [$SQLDatabase].[dbo].[$Tablename]";
$SQLquery;
[/sourcecode]
2. Using Here-String/Splatting, you can change the above sample and make it a multi-line string. This still is a One-liner, and it use the tab in front of the column names. *note: In PowerShell V3.0 the tab will be ignore but in PowerShell V2.0 it will work OK.
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
## [2] – Using Here-String/Splatting. This string contains manual tabs done in and editor the it was copy/paste to the console: (bug in V3 console only. ISE works.)
$SQLquery1 = @"
Select
[firstname],
[lastname]
from [$SQLDatabase].[dbo].[$Tablename]
"@;
$SQLquery1;
Write-Host "$SQLquery1" -ForegroundColor ‘Yellow’;
[/sourcecode]
3. The last Here-String sample we are using the .NET ‘-f’ string formatter which will allow you to replace the values for {0} and {1} place holder. In this sample code inside the string i’m hard coding tab as `t (tick symbol plus t) which in this case it works OK in both PowerShell V2 and V3:
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
## [3] – Using Here-String/Splatting with .NET ‘-f’ formatting:
$SQLquery2 = @"
Select
`t[firstname],
`t[lastname]
from [{0}].[dbo].[{1}]
"@ -f $SQLDatabase, $tablename;
Write-Host "$SQLquery2" -ForegroundColor ‘Cyan’;
[/sourcecode]
4. When using a PowerShell editor (ISE or others) an invalid Here-String variable PowerShell will give an error if you try to use tabs on each line of the code: (can’t use white space in editor with Here-String)
[tab] $x = @”
[tab] Testing
[tab] Testing
[tab] “@;
Basically, Here-String variable works great when you want to store a multi-line string but have some caveats:
1. PowerShell v3 console only. Manual tabs are ignored.
2. When using splatting (@”..”@) the @” can begin in any column position but the terminating “@ ends on the beginning of the new line. See sample #3.
3. When using a PowerShell editor Whitespaces in a Here-String block of code are not allowed.
Once again, another great Saturday IT Pro event at Keiser University in Sarasota, Florida. It was awesome to see some great speakers giving their sessions, and I got to meet Pinal Dave which is pretty well known in the SQL Server Community Worldwide. See below picture (Me and Pinal Dave).
Microsoft IT Pro Evangelist Blain Barton put together a great Windows Azure session with Herve Roggero (Windows Azure MVP). See below picture.
Thank You all for attending my PowerShell Working with .NET PSObject session. Here’s is my full presentation with all the PowerShell scripts I meant to cover. Please feel free to try them out. During our session I was able to cover only one of the three Excel PowerShell sample.
Thank You Kieser University for having us!
As I look for a way that I could eliminate a single or a range of elements, I found many C# .NET code on how do it. But only one of the answer in many caught my eye. This answer was “System.Collections.ObjectModel.Collection“. This help me search deeper and of course found that there’s a couple of methods I could use if I create my Array as an ArrayList type.
This way I got available two methods I can use: .RemoveAt( element# ) and .RemoveRange( AtElement# , HowMany# ) .
So, in scenario where you want to remove some elements of the array in PowerShell try using the following typed accelerator [System.Collections.ArrayList] .
Here’s a basic sample code:
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
## – creating your Arraylist .NET object and creates 20 elements:
[System.Collections.ArrayList] $b = 1..20;
## – Here’s how you verify the type of object you created:
$b.GetType()
## – This example will remove Array element #4 and display the results:
$b.RemoveAt(4);
$b
## – This example will remove a range of 3 elements starting at element #7:
$b.removerange(7,3)
$b
[/sourcecode]
It’s all part of the beauty of .NET with PowerShell!
While working on my PowerShell demo scripts today, I decided to create a simple function to display my scripts during my presentations. Here’s my new and simple Show-PSDemo function:
[sourcecode language=”powershell”]
#========================================================================
# Created with: SAPIEN Technologies, Inc., PowerShell Studio 2012 v3.1.15
# Created on: 1/13/2013 9:07 AM
# Created by: Maximo Trinidad
# Organization: PutItTogether
# Filename: Show-PSDemo_function.ps1
# Version: 0.1
#========================================================================
function Show-PSDemo{
Param([String] $FileLocation)
## – Verify for a valid file location:
if((Test-Path -Path $FileLocation) -ne $true)
{
Write-Host "No script files to execute!" `
-ForegroundColor ‘Yellow’;
Break;
}
else
{
[Array] $executethis = Get-Content $FileLocation;
};
## – Saved previous default Host Colors:
$defaultForegroundColor = $host.UI.RawUI.ForegroundColor;
$defaultBackgroundColor = $host.UI.RawUI.BackgroundColor;
## – Customizing Host Colors:
$host.UI.RawUI.ForegroundColor = "Cyan";
$host.UI.RawUI.BackgroundColor = "Black";
$StartDemoTime = [DateTime]::now; $i = 0;
Clear-Host;
Write-Host "Demo Start Time: $([DateTime]::now)" -ForeGroundColor ‘White’;
Write-Host "`t Running Script file: $FileLocation" -ForegroundColor ‘Yellow’;
foreach($line in $executethis)
{
$i++
## – Identify comment lines:
if($line.Startswith(‘#’)){
Write-Host -NoNewLine $("`n[$i]PS> ")
Write-Host -NoNewLine -Foreground ‘Green’ $($($line) + " ")
}
Else
{
## – add section identify oneliners with continuation tick:
[string] $Addline = $null;
if($line -match ‘`’)
{
#Write-Host " Found tick = `t`r`n $($line)" -ForegroundColor yellow;
$Addline = $line.replace(‘`’,”).tostring();
$Scriptline += $Addline;
$tickFound = $true;
$continuation = $true;
## – List oneliner with continuation tick:
Write-Host -NoNewLine $("`n[$i]PS> ");
Write-Host -NoNewLine $line;
}
else
{
## – identify the last line of a continuation oneliner:
if($tickFound -eq $true)
{
$Scriptline += $line;
$tickFound = $false;
$continuation = $false;
## – List oneliner with continuation tick:
Write-Host -NoNewLine $("`n[$i]PS> ");
Write-Host -NoNewLine $line "`r`n";
}
Else
{
## – Single onliner found:
$Scriptline = $line;
$continuation = $false;
Write-Host -NoNewLine $("`n[$i]PS> ")
Write-Host -NoNewLine $Scriptline "`r`n";
};
};
if($continuation -eq $false)
{
## – Executive:
Write-Host "`r`n`t Executing Script…`r`n" -ForegroundColor ‘Yellow’;
Invoke-Expression $(‘.{‘ +$Scriptline + ‘}| out-host’);
$Scriptline = $null;
}
## – ——————————————————————–
if($continuation -eq $false)
{
Write-Host "`r`n– Press Enter to continue –" -ForegroundColor ‘Magenta’ `
-BackgroundColor white;
Read-Host;
};
};
};
$DemoDurationTime = ([DateTime]::Now) – $StartDemoTime;
Write-Host ("`t <Demo Duration: {0} Minutes and {1} Seconds>" `
-f [int]$DemoDurationTime.TotalMinutes, [int]$DemoDurationTime.Seconds)
-ForeGroundColor ‘Yellow’ ;
Write-Host "`t Demo Completed at: $([DateTime]::now))" -ForeGroundColor ‘White’;
## – Set back to Default Color:
$host.UI.RawUI.ForegroundColor = $defaultForegroundColor;
$host.UI.RawUI.BackgroundColor = $defaultBackgroundColor;
};
## – loading:
## . .\Temp\Show-PSDemo_Function.ps1
## Show-PSdemo -FileLocation C:\temp\PowerShell_SQLdata.ps1
[/sourcecode]
It has one parameter “-FileLocation” which is you full folder and file location. The file extension doesn’t matter as long is a text file with PowerShell code in it.
It allows to:
1. The use of Comments lines.
2. The use of the “$_” in a “Select-Object“.
3. Allows the use of the “`” tick which identify a line continuation.
4. A “Pause” is included after executing each line or block of code.
Simple to load as a function, then execute:
PS C:\> . .\YourScriptFolder\Show-PSDemo_function.ps1
PS C:\> Show-PSDemo -FileLocation C:\YourScriptFolder\MyDemoScript.ps1
It works in both PowerShell Console and PowerShell ISE editor.