Just to be clear!! You can run PowerShell in SQL Server Management Studio.
Not only you can run PowerShell, but you can create scheduled jobs in SQL Agent to run PowerShell scripts. This has been available since SQL Server 2008 (before R2). And, this is a lot better now, as each version are finally providing more “SQL PowerShell cmdlets” to manage your SQL Server in their *”SQLPS” PowerShell module.
*Note: SQLPS Module was introduce with SQL Server 2008.
Nowadays, Thanks to both Aaron Nelson, Christy LeMaire, and Rob Sewell who have contribute to the success of provide new enhancements to SQL Server PowerShell (SQLPS) cmdlets. Check out their tools:
DBA Tools “best practices and instance migration module” link: https://dbatools.io/
DBA Reports “free, fun” link: https://dbareports.io/
By the way, DBA Reports is owned by Rob Sewell – @sqldbawithabeard. Great Work!!
So, YES! You can run PowerShell from SQL Server Management Studio.
How to run PowerShell?
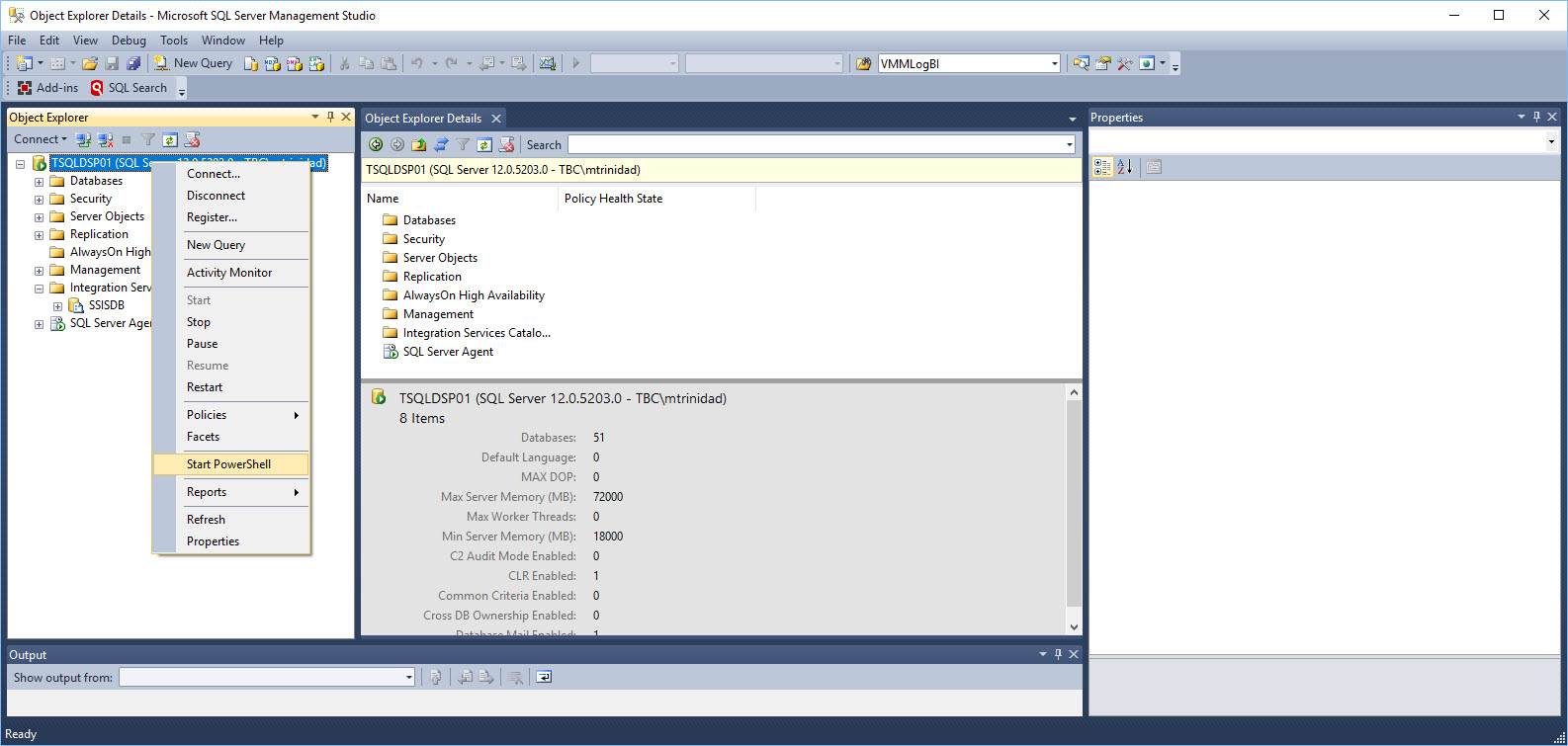
You can Right-Click on most of the SQL Server objects under “Object Explorer” and look for “Start PowerShell“.
This will open the PowerShell prompt and you are ready to start your adhoc scripting.
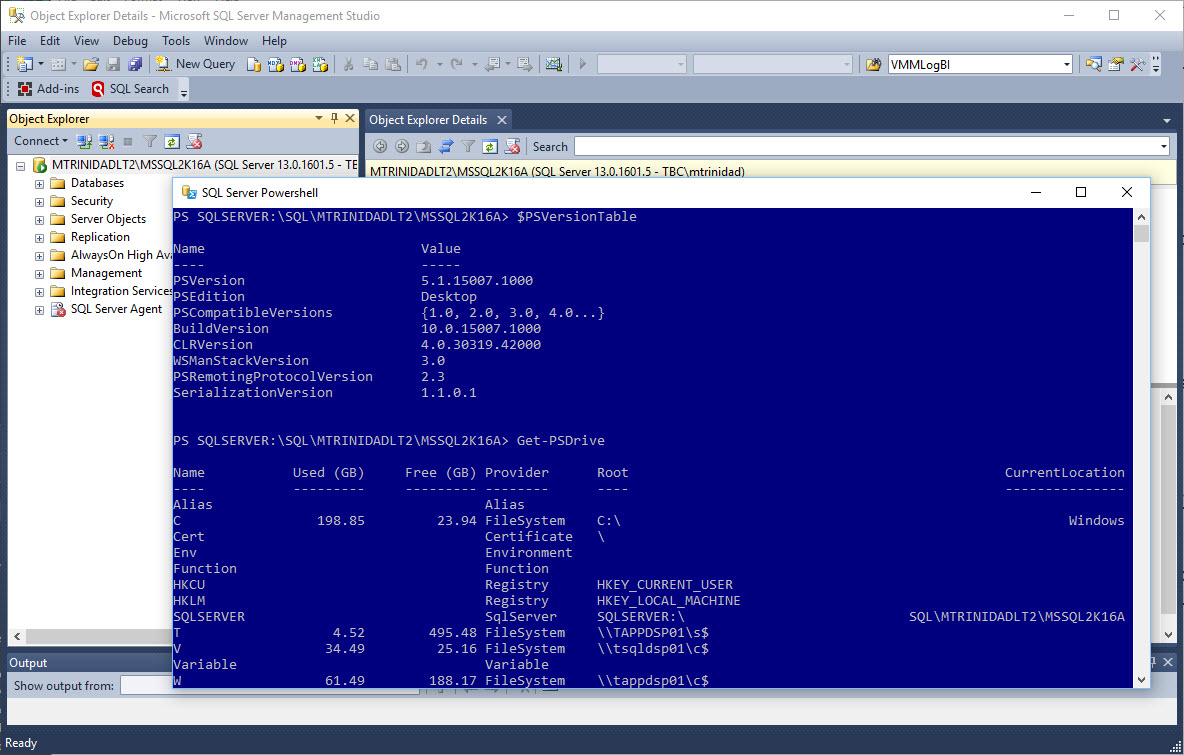
Keep in mind, on the latest version of SQL Server (< 2012), the SQL PowerShell module (SQLPS) is loaded and already available. This will create a SQL Server Drive connecting (in this case) to your local instance installation or whichever instance you’re connecting to.
Notice, in my case, the above image will open a PowerShell prompt and is using PowerShell version 5.1 which is part of my Windows 10. The same will be true on earlier OS version of PowerShell. The “Start PowerShell” will open the current PowerShell version installed on that machine.
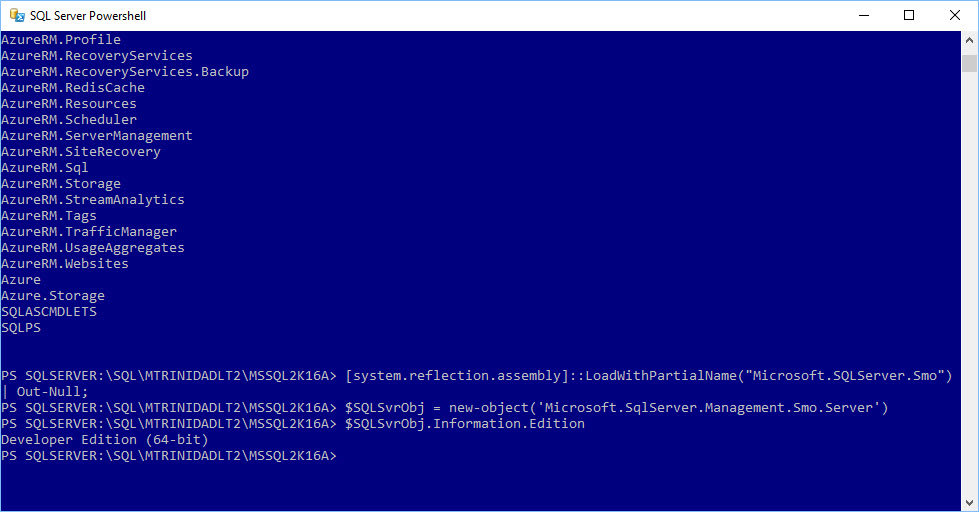
Another thing to understand, although you already have a set of available cmdlets to manage your SQL Server, you can still expand and build more script with the use SMO (SQL Server Management Objects). So, the possibilities to build your own solutions are endless.
All SMO .NET assemblies are loaded into your system when installing SSMS.
About SQLPS been removed
To be clear! Documentation states that SQLPS “Utility” (sqlps.exe) will be removed in the future. But, the SQLPS PowerShell module will still be available. (See reference link)
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc280450(v=sql.130).aspx
This is why you rather use the normal PowerShell console and start using the SQLPS module. Keep in mind, that since PowerShell 3.0, all existing installed modules are automatically loaded and ready to use in your PowerShell session.
How do I get SQL PowerShell?
Simple! SQL PowerShell comes included when SQL Server Management Studio(SSMS) is installed. For sometime ago SSMS (SSMS 2012) has been available to install separately (free-of-charge). As a matter of fact, you could install three separate SQL Server Features components without the need of installing SSMS and start scripting against your SQL engine.
The following link shows both latest version of SSMS (16.5.3) and the preview SSMS for SQL Server vNext (RC 17) can be found here:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/ssms/download-sql-server-management-studio-ssms
Bonus – No need for SSMS GUI nor the SQL Engine
Sometimes there’s no need to install a SQL instance, nor SSMS GUI but only the necessary components installed in order to run and scheduled some SQL PowerShell scripts in Windows Server Task Scheduler. I had this scenario on a **server with no SQL engine but needed to run some scheduled SQL PowerShell scripts. Only 3 components are needed:
(Below content extracted from Microsoft link (Install section) : https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=52676 )
– Microsoft® Windows PowerShell Extensions for Microsoft SQL Server® 2016
The Microsoft Windows PowerShell Extensions for SQL Server includes a provider and a set of cmdlets that enable administrators and developers to build PowerShell scripts for managing instances of SQL Server. The SQL Server PowerShell Provider delivers a simple mechanism for navigating SQL Server instances that is similar to file system paths. PowerShell scripts can then use the SQL Server Management Objects to administer the instances. The SQL Server cmdlets support operations such as executing Transact-SQL scripts or evaluating SQL Server policies.
Filename: X86 and x64 Package (PowerShellTools.msi)
– Microsoft® SQL Server® 2016 Shared Management Objects
SQL Server Management Objects (SMO) is a .NET Framework object model that enables software developers to create client-side applications to manage and administer SQL Server objects and services.
Note: Microsoft SQL Server Management Objects requires – Microsoft SQL Server System CLR Types, that is available on this page.
Filename: X86 and x64 Package (SharedManagementObjects.msi)
– Microsoft® System CLR Types for Microsoft SQL Server® 2016
The SQL Server System CLR Types package contains the components implementing the geometry, geography, and hierarchy id types in SQL Server. This component can be installed separately from the server to allow client applications to use these types outside of the server.
Filename: X86 and x64 Package (SQLSysClrTypes.msi)
**Note: This can apply to desktop/laptop is you don’t want to install the whole SQL Server CD. As long as, you have remote connection to a SQL Server system, then you just start building scripts. You will save some disk space too.